我们有一个使用 TM4C1292NCPDT的定制电路板。
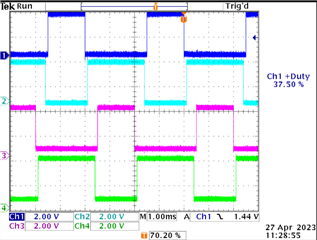
该板将使用两个交错式 PWM 信号对。 目前、我以向上/向下模式运行 PWM 第0代和 PWM 第1代。 是否可以使用 TISW API 来偏移发生器模块使其180度相位差? 例如、在下图中、我希望 L1和 L2具有180度的相位差、H1和 H2具有180度的相位差、同时保持相同的占空比。 软件 API 中是否有方法可以设置其中一个生成器的起始计数来实现该目的? 占空比会在运行时发生变化、因此需要是真正的180度相移(而不是反转50%占空比信号)。

这是相应的初始化代码:
#define GENERATOR_PERIOD_COUNTS 1000 #define DEAD_BAND_DURATION_COUNTS 50 SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOF); while(!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOF)); // Configure the GPIO for PWM peripheral use. GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF0_M0PWM0); GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF1_M0PWM1); GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF2_M0PWM2); GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF3_M0PWM3); GPIOPinTypePWM(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0); GPIOPinTypePWM(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1); GPIOPinTypePWM(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2); GPIOPinTypePWM(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3); SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_PWM0); // enable the pwm peripheral while(!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_PWM0)); // wait for the peripheral to be ready PWMClockSet(PWM0_BASE, PWM_SYSCLK_DIV_1); // Sets the PWM clock configuration to use the system clock with a divider of 1 /* * Configure generator blocks to run in up/down mode which allows * use of the built-in dead band time. In this mode, the synchronization of * the 2 signals in each generator are synchronized by default, so we * don't need to set any. */ PWMGenConfigure(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_0, PWM_GEN_MODE_UP_DOWN | PWM_GEN_MODE_NO_SYNC); PWMGenConfigure(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_1, PWM_GEN_MODE_UP_DOWN | PWM_GEN_MODE_NO_SYNC); /* * Set the PWM period. Configures the reference counter that counts in up/down mode. * * f = PWM_ref_clk / N ... where f is the desired frequency, N is the passed param, * and PWM_ref_clk is the reference clock. */ PWMGenPeriodSet(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_0, GENERATOR_PERIOD_COUNTS); PWMGenPeriodSet(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_1, GENERATOR_PERIOD_COUNTS); /* * Enables dead band generation with a configurable buffer on both the rising and falling * edge of the signals. Enabling this will automatically synchronize the signal pairs in * each of the generator blocks. */ PWMDeadBandEnable(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_0, DEAD_BAND_DURATION_COUNTS, DEAD_BAND_DURATION_COUNTS); PWMDeadBandEnable(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_1, DEAD_BAND_DURATION_COUNTS, DEAD_BAND_DURATION_COUNTS); PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM0_BASE, PWM_OUT_0, 550); // complement signal PWM_OUT_1 updates automatically PWMPulseWidthSet(PWM0_BASE, PWM_OUT_2, 550); // complement signal PWM_OUT_3 updates automatically PWMGenEnable(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_0); PWMGenEnable(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_1); PWMSyncTimeBase(PWM0_BASE, PWM_GEN_1_BIT | PWM_GEN_0_BIT); PWMOutputState(PWM0_BASE, PWM_OUT_2_BIT | PWM_OUT_3_BIT | PWM_OUT_0_BIT | PWM_OUT_1_BIT, true);