作者:Terry Deng
本文档概述了一种基于 SCI/UART 输入信号,可以自动校准本设备SCI/UART波特率的方法,该方法适用与所有第三代C2000芯片,比如F2807x/37x,F28004x,F28002x等等。
一 原理说明
假设有2块电路板通过SCI进行通信。“Transmitter”向“Receiver”发送未知波特率的数据,“ Receiver”则使用 eCAP 测量未知的波特率,然后修改其自身的波特率和“Transmitter”匹配。
下面款图是一种情况,其中“Transmitter” 的波特率设置为 9889,而“Receiver”的初始波特率设置为 9601 ,相比之下“Receiver”的波特率为 -3% 偏差。 经过算法的自动校准以后,“Receiver”将会把自身波特率校正为与“Transmitter”相同的9889。
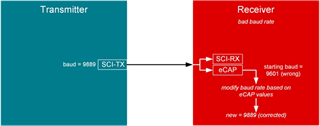
下面框图则是另一种情况,假如“Receiver”和“Transmitter”的初始波特率都是9889,但“Receiver”的内部晶振INTOSC有-3%的偏差。使用上述完全相同的方法原理和步骤,“Receiver”波特率设置将会从9889校准成9601,这样“Receiver”的波特率设置被自动校准抵消内部晶振的偏差。在测量实际信号时,“Receiver”输出到“Transmitter”的信号会是正确的 9889 波特率。
二 Receiver 的校准代码
1. 初始化
需要配置以下模块来校准波特率:
- 时钟:使用 INTOSC2 并选择 100MHz 的 LSPCLK
#define DEVICE_SETCLOCK_CFG (SYSCTL_OSCSRC_OSC2 | SYSCTL_IMULT(20) | \
SYSCTL_FMULT_NONE | SYSCTL_SYSDIV(2) | \
SYSCTL_PLL_ENABLE)
//
// Set up PLL control and clock dividers
//
SysCtl_setClock(DEVICE_SETCLOCK_CFG);
//
// Make sure the LSPCLK divider is set to the default (divide by 4)
//
SysCtl_setLowSpeedClock(SYSCTL_LSPCLK_PRESCALE_1);
- SCI 模块:通讯数据使用,发出校准以后的波形
// Initialize SCIA and its FIFO.
//
SCI_performSoftwareReset(SCIA_BASE);
//
// Configure SCIA for communications.
//
SCI_setConfig(SCIA_BASE, DEVICE_LSPCLK_FREQ, TARGETBAUD, (SCI_CONFIG_WLEN_8 |
SCI_CONFIG_STOP_ONE |
SCI_CONFIG_PAR_NONE));
SCI_resetChannels(SCIA_BASE);
SCI_resetRxFIFO(SCIA_BASE);
SCI_resetTxFIFO(SCIA_BASE);
SCI_clearInterruptStatus(SCIA_BASE, SCI_INT_TXFF | SCI_INT_RXFF);
SCI_enableFIFO(SCIA_BASE);
SCI_enableModule(SCIA_BASE);
SCI_performSoftwareReset(SCIA_BASE);
- Xbar 输入:将 GPIO28/SCI 内部连接到 INPUTXBAR7 与 ECAP1 配合使用
//
// Configure GPIO 28 as eCAP input
//
XBAR_setInputPin(XBAR_INPUT7, 28);
- ECAP 模块:监控接收到的 SCI 通信脉冲宽度
//
// Disable ,clear all capture flags and interrupts
//
ECAP_disableInterrupt(ECAP1_BASE,
(ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_1 |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_2 |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_3 |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_4 |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_COUNTER_OVERFLOW |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_COUNTER_PERIOD |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_COUNTER_COMPARE));
ECAP_clearInterrupt(ECAP1_BASE,
(ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_1 |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_2 |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_3 |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_4 |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_COUNTER_OVERFLOW |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_COUNTER_PERIOD |
ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_COUNTER_COMPARE));
//
// Disable CAP1-CAP4 register loads
//
ECAP_disableTimeStampCapture(ECAP1_BASE);
//
// Configure eCAP
// Enable capture mode.
// One shot mode, stop capture at event 4.
// Set polarity of the events to rising, falling, rising, falling edge.
// Set capture in time difference mode.
// Select input from XBAR7.
// Enable eCAP module.
// Enable interrupt.
//
ECAP_stopCounter(ECAP1_BASE);
ECAP_enableCaptureMode(ECAP1_BASE);
ECAP_setCaptureMode(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_ONE_SHOT_CAPTURE_MODE, ECAP_EVENT_4);
ECAP_setEventPolarity(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_1, ECAP_EVNT_FALLING_EDGE);
ECAP_setEventPolarity(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_2, ECAP_EVNT_RISING_EDGE);
ECAP_setEventPolarity(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_3, ECAP_EVNT_FALLING_EDGE);
ECAP_setEventPolarity(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_4, ECAP_EVNT_RISING_EDGE);
ECAP_enableCounterResetOnEvent(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_1);
ECAP_enableCounterResetOnEvent(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_2);
ECAP_enableCounterResetOnEvent(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_3);
ECAP_enableCounterResetOnEvent(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_4);
ECAP_selectECAPInput(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_INPUT_INPUTXBAR7);
ECAP_enableLoadCounter(ECAP1_BASE);
ECAP_setSyncOutMode(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_SYNC_OUT_DISABLED);
ECAP_startCounter(ECAP1_BASE);
ECAP_enableTimeStampCapture(ECAP1_BASE);
ECAP_reArm(ECAP1_BASE);
ECAP_enableInterrupt(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_4);
2. 中断
捕获传入 SCI 通信的脉冲宽度,每捕获 4 次就中断一次。 将这 4 个捕获添加到阵列中。
__interrupt void ecap1ISR(void)
{
if(stopCaptures==0)
{
//
// Get the capture counts, interrupt every 4. Can be 1-bit or more wide.
// add one to account for partial eCAP counts at higher baud rates
// (e.g. count = 40, but if had higher resolution, this would be 40.5)
//
capCountArr[0] = 1+ECAP_getEventTimeStamp(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_1);
capCountArr[1] = 1+ECAP_getEventTimeStamp(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_2);
capCountArr[2] = 1+ECAP_getEventTimeStamp(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_3);
capCountArr[3] = 1+ECAP_getEventTimeStamp(ECAP1_BASE, ECAP_EVENT_4);
//
// Add samples to a buffer. Get average baud and tune INTOSC if buffer filled.
//
capCountIter = 0;
for (capCountIter=0; capCountIter<4; capCountIter++)
{
//
// if we still have samples left to capture, add it to the samples array
//
if(samplesArrIter<NUMSAMPLES)
{
samplesArr[samplesArrIter] = capCountArr[capCountIter];
samplesArrIter++;
}
//
// else, all samples were received, break to begin tuning
//
else
{
stopCaptures=1;
break;
}
}
}
//
// Clear interrupt flags for more interrupts.
//
ECAP_clearInterrupt(ECAP1_BASE,ECAP_ISR_SOURCE_CAPTURE_EVENT_4);
ECAP_clearGlobalInterrupt(ECAP1_BASE);
//
// Start eCAP
//
ECAP_reArm(ECAP1_BASE);
//
// Acknowledge the group interrupt for more interrupts.
//
Interrupt_clearACKGroup(INTERRUPT_ACK_GROUP4);
}
3. 主循环
捕获阵列满后,计算阵列的平均脉冲宽度 (也就是波特率),并更新SCI波特率寄存器,使其尽可能接近计算的平均值。
//
// Loop forever. Suspend or place breakpoints to observe the buffers.
//
for(;;)
{
//
// Array is filled, begin tuning
//
if(stopCaptures==1)
{
//
// Get an average baud rate from the array of samples
//
uint32_t avgBaud = getAverageBaud(samplesArr,NUMSAMPLES,TARGETBAUD);
//
// if the baud function returns the error code '0', then flag an error
//
if(avgBaud==0)
{
ESTOP0;
}
//
// Update the device's baud rate to match the measured baud rate
//
SCI_setBaud(SCIA_BASE, DEVICE_LSPCLK_FREQ, avgBaud);
//
// (OPTIONAL) Continuously send data to SCITX once tuning
// is complete for external observation (by logic analyzer or scope)
//
//unsigned char *msg;
//while(1)
//{
// msg = "aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa\0";
// SCI_writeCharArray(SCIA_BASE, (uint16_t*)msg, 91);
//}
//
// Wait for user to view the results in "Expressions" window
//
ESTOP0;
//
// If continuing, reset the array iterator and unlock the ISR for new captures
//
samplesArrIter=0;
stopCaptures=0;
}
}
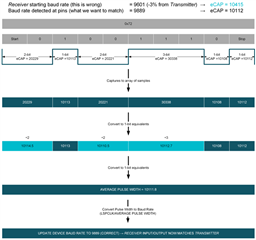
4. 平均脉冲宽度
对于许多应用的SCI 通信,传输的数据 (例如 0xA5)是变化不固定的,因此SCI的高低电平脉冲宽度就是变化的。所以必须对样本阵列进行如下的预处理,然后才能计算平均脉冲宽度。
a) 丢弃大于 10 位宽的脉冲宽度 (丢弃空闲时间)
b) 将 n 位值除以 n
c) 对修改后的样本数组进行平均化
uint32_t getAverageBaud(volatile float arr[], int size, float targetBaudRate)
{
//
// clean up variable width array to single-bit-width array
//
uint16_t pass = arrTo1PulseWidth(arr, size, (float)DEVICE_SYSCLK_FREQ/targetBaudRate);
//
// pass only if enough good samples provided
//
if(pass == 0)
{
return 0;
}
//
// convert 2-bit width, 3-bit width, etc. to 1-bit width values by dividing, and average these values.
// skip unrelated values
//
float averageBitWidth = computeAvgWidth(arr, size);
//
// get the rounded baud rate from the average number of clocks and the sysclk frequency
//
return (uint32_t)(((float)DEVICE_SYSCLK_FREQ/(float)averageBitWidth)+0.5);
}
以下是平均脉宽计算的原理和代码流程图

三 结果
按照以下设置进行测试,结果详见表格,校准以后的误差从3% 改善为0.1%左右甚至更小。
- “Transmitter”设置为正确的波特率 (我们尝试匹配的波特率)
- “Receiver”设置为错误波特率 (-3% 或 +3%)
- “Receiver”运行校准程序以匹配“Transmitter”
|
|
100K 波特率 |
9601波特率 |
|||
|
-3% |
+3% |
-3% |
+3% |
||
|
Transmitter (我们正在尝试匹配的内容) |
理想波特率 (仅供参考) |
103306 |
96899 |
9889 |
9314. |
|
实际波特率 (必须与此匹配) |
104174. |
96906 |
9890 |
9315. |
|
|
Receiver (初始错误波特率) |
波特率 (校准前) |
100154. |
100157. |
9622. |
9622. |
|
出错百分比 (校准前) |
-3.859% |
3.355% |
-2.706% |
3.296% |
|
|
Receiver (校准后波特率) |
波特率 (校准后) |
104336. |
97047. |
9888 |
9314. |
|
出错百分比 (校准后) |
0.156% |
0.146% |
-0.016% |
-0.012% |
|
