如题,
使用28377D调试CAN通讯,
初始化给定ID后,就只能接收到初始化对应ID的数据,其他ID的数据都接收不到。
ID过滤的相关寄存器已经赋值为0;
IDMASK = 0; UMASK=0;
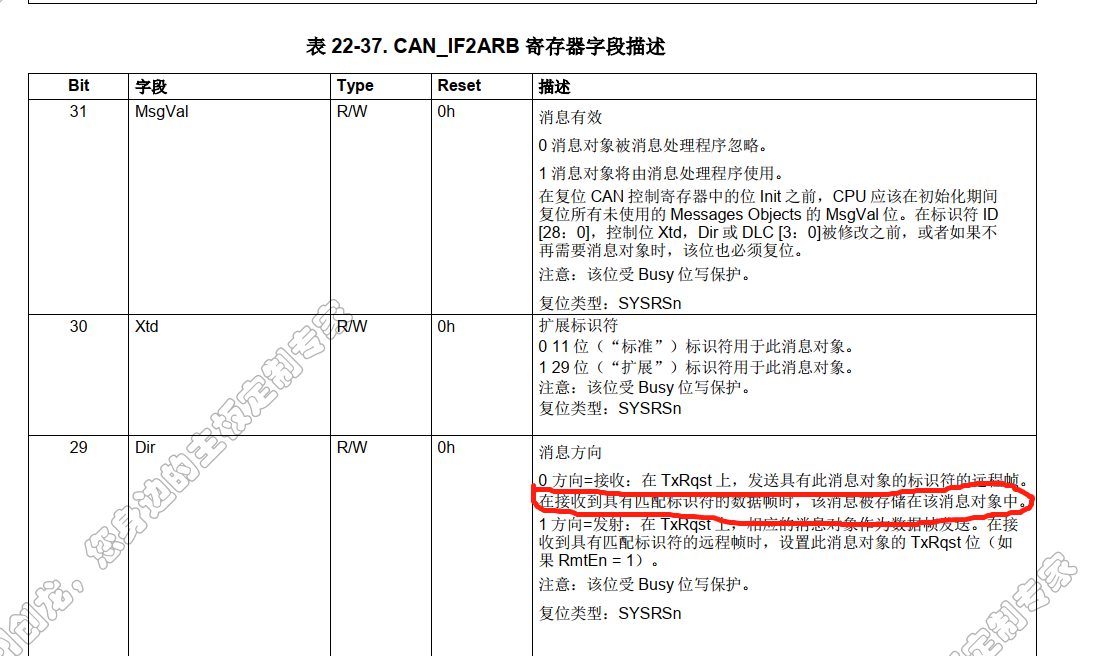
看了一下数据手册,IFxARB->Dir的介绍,
| 0 Direction = receive: On TxRqst, a remote frame with the identifier of this message object is transmitted. On reception of a data frame with matching identifier, that message is stored in this message object. |
接收到匹配标识符的数据帧时,消息才会存储?
是不是就这个原因?只能接收对应初始化时ID的数据,如果是的话,怎么设置才能接收任意ID数据?
有知道的帮忙回答一下,TKS
仿真打断点,读取寄存器的值,