主题中讨论的其他器件:TM4C123GH6PM、 TM4C123、 ENERGIA
您好!
我尝试通过 I2C 传输数据。 但是、我似乎无法使它正常工作。
使用 CCS 版本10.3.0.00007,我在 TI 提供的外设用户指南的16.3下复制了编程示例,请参阅链接:
我将随附我的代码:
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "driverlib/fpu.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/rom.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/timer.h"
#include "driverlib/i2c.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The error routine that is called if the driver library encounters an error.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
}
#endif
void ConfigureI2CasMaster()
{
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0);
while (!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_I2C0))
{
}
// set bus speed and enable master
I2CMasterInitExpClk(I2C0_BASE, SysCtlClockGet(), true);
I2CMasterSlaveAddrSet(I2C0_BASE, 0x3B, false);
I2CMasterDataPut(I2C0_BASE, 'Q');
I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
while (I2CMasterBusBusy(I2C0_BASE))
{
}
}
void SendI2CData()
{
I2CMasterDataPut(I2C0_BASE, 'Q');
I2CMasterControl(I2C0_BASE, I2C_MASTER_CMD_SINGLE_SEND);
while (I2CMasterBusBusy(I2C0_BASE))
{
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// main
//
//*****************************************************************************
int main(void)
{
// Setup the system clock to run at 40 MHz from PLL with crystal reference
ROM_SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_5 | SYSCTL_USE_PLL | SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN);
ConfigureI2CasMaster();
// enter the Loop
while (1)
{
SysCtlDelay(10000);
SendI2CData();
}
}
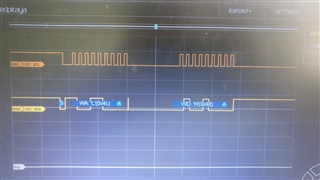
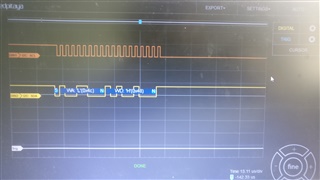
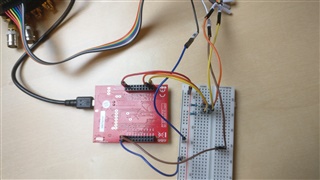
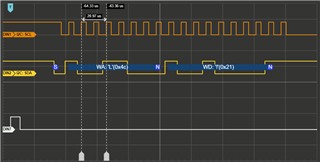
我在引脚 B2和 B3上有一个逻辑分析仪、这是 TM4C123GXL 板上的 SCL0和 SDA0。
GND 已连接、逻辑分析仪已正确设置。 (在不同器件上测试)
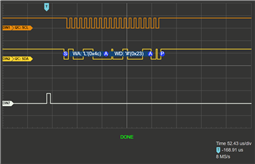
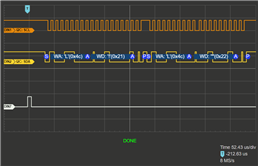
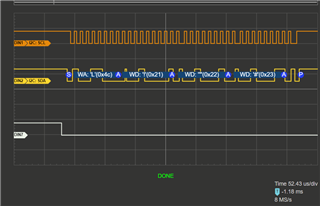
我希望我的代码能够重复传输数据、但我的逻辑分析仪却显示完全没有发生任何事情。
我的代码有什么问题吗?
谢谢你