我需要将 EK-TM4C1294XL 用作 SPI 从设备(SSI2端口)。 来自主器件的数据以1MHz 的频率传入一个包含8个16字节(总共128位)寄存器的数据包。 新 CS 之间的时间很短、数据会连续传输。
如何才能在 EK-TM4C1294XL 上获取此数据并将其正确解析到寄存器中?
我想在 TI-RTOS 中工作。
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
我需要将 EK-TM4C1294XL 用作 SPI 从设备(SSI2端口)。 来自主器件的数据以1MHz 的频率传入一个包含8个16字节(总共128位)寄存器的数据包。 新 CS 之间的时间很短、数据会连续传输。
如何才能在 EK-TM4C1294XL 上获取此数据并将其正确解析到寄存器中?
我想在 TI-RTOS 中工作。
您好!
如果 您正在快速接收数据、则 可以在中断模式下操作、在 RXFIFO 为半满或更多时会生成中断。 在 RX ISR 中、您可以并行处理传入的数据、而更多的数据来自主器件。
我们没有一个纯粹的 SSI 从站示例。 我建议您参考 TI-RTOS SPI 环回示例作为起点、并 针对您的应用进行必要的更改。 此示例将使用 TI-RTOS SPI 驱动程序。
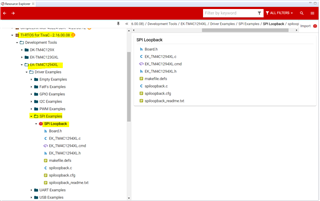
如果您想使用 TivaWare SPI 驱动程序、那么您也可以查看示例、例如 C:\ti\TivaWare_C_Series-2.2.0.295\examples\boards\ek-tm4c1294xl\ssi_master_slave_xfer。
我使用示例 SSI_MASTER_SLAVE_xfer。 我尝试10次以获得相同的序列、但每次我得到一个包含8个元素的新数组...
void
SSI2IntHandler(void)
{
uint32_t ui32Status;
//
// Read SSIMIS (SSI Masked Interrupt Status).
//
ui32Status = MAP_SSIIntStatus(SSI2_BASE, true);
//
// Clear the SSI interrupt.
//
MAP_SSIIntClear(SSI2_BASE, ui32Status);
//
// Turn off the RX FIFO interrupt.
//
MAP_SSIIntDisable(SSI2_BASE, SSI_RXFF);
g_breceiveFlag = 1;
}
int t=0;
while (t<10)
{
//
// Wait until SSI1 receives the half-full interrupt on the RX FIFO.
//
while (g_breceiveFlag == 0);
//
// Display indication that the SSI0 is receiving data.
//
//
// Receive 4 bytes of data.
//
for(ui32Index = 0; ui32Index < NUM_SSI_DATA; ui32Index++)
{
//
// Receive the data using the "blocking" Get function. This function
// will wait until there is data in the receive FIFO before returning.
//
MAP_SSIDataGet(SSI2_BASE, &pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
//
// Since we are using 16-bit data, mask off the MSB.
//
//pui32DataRx[ui32Index] &= 0xFFFF;
//
// Display the data that SSI0 received.
//
//UARTprintf("'%d' ", pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
}
UARTprintf("\nSSI2 Received: '%d' \n", t);
for(ui32Index = 0; ui32Index < NUM_SSI_DATA; ui32Index++)
{
pui32DataRx[ui32Index] &= 0xFFFF;
//
// Display the data that SSI0 received.
//
UARTprintf("'%d' ", pui32DataRx[ui32Index]);
}
UARTprintf("\n\nMaster-Slave Transfer Complete.\n");
//
// Display indication that the SSI1 is receiving data.
//
t++;
}
SSI2 Received: '1' '43250' '43251' '43252' '43253' '43254' '43255' '43256' '43249' Master-Slave Transfer Complete. SSI2 Received: '2' '43253' '43254' '43255' '43256' '43249' '43250' '43251' '43252' Master-Slave Transfer Complete. SSI2 Received: '3' '43249' '43250' '43251' '43252' '43253' '43254' '43255' '43256' Master-Slave Transfer Complete. SSI2 Received: '4' '43252' '43253' '43254' '43255' '43256' '43249' '43250' '43251' Master-Slave Transfer Complete. SSI2 Received: '5' '43256' '43249' '43250' '43251' '43252' '43253' '43254' '43255' Master-Slave Transfer Complete. SSI2 Received: '6' '43252' '43253' '43254' '43255' '43256' '43249' '43250' '43251' Master-Slave Transfer Complete. SSI2 Received: '7' '43255' '43256' '43249' '43250' '43251' '43252' '43253' '43254' Master-Slave Transfer Complete. SSI2 Received: '8' '43251' '43252' '43253' '43254' '43255' '43256' '43249' '43250' Master-Slave Transfer Complete. SSI2 Received: '9' '43254' '43255' '43256' '43249' '43250' '43251' '43252' '43253' Master-Slave Transfer Complete.
主器件阵列:'43249'43250''43251''43252''43254'43254'43255''43256'
波形:
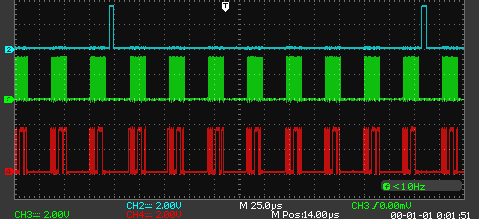
您好!
有关设置 Hwi 的详细信息、请转到本 TI-RTOS 实验课程培训中的第5节"使用 Hwi "。 第166页提供了为 Tiva MCU 设置 Hwi 的示例。
https://training.ti.com/sites/default/files/docs/TI_RTOS_Kernel_Workshop_Student_Guide_rev4.00.pdf
下面是为 Timer2A 设置 Hwi 的示例。
//----------------------------------------
// BIOS header files
//----------------------------------------
#include <xdc/std.h> //mandatory - have to include first, for BIOS types
#include <ti/sysbios/BIOS.h> //mandatory - if you call APIs like BIOS_start()
#include <xdc/runtime/Log.h> //needed for any Log_info() call
#include <xdc/cfg/global.h> //header file for statically defined objects/handles
#include <xdc/runtime/System.h>
#include <xdc/runtime/Error.h>
#include <ti/sysbios/hal/Hwi.h>
//------------------------------------------
// TivaWare Header Files
//------------------------------------------
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/timer.h"
//----------------------------------------
// Prototypes
//----------------------------------------
void hardware_init(void);
void ledToggle(void);
//---------------------------------------
// Globals
//---------------------------------------
volatile int16_t i16ToggleCount = 0;
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// main()
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void main(void)
{
hardware_init(); // init hardware via Xware
Hwi_Params hwiParams;
Hwi_Handle myHwi;
Error_Block eb;
/* Initialize error block and hwiParams to default values */
Error_init(&eb);
Hwi_Params_init(&hwiParams);
hwiParams.enableInt = FALSE;
myHwi = Hwi_create(39, (Hwi_FuncPtr)ledToggle, &hwiParams, &eb);
if (myHwi == NULL) {
System_abort("Hwi create failed");
}
Hwi_enableInterrupt(39);
BIOS_start();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// hardware_init()
//
// inits GPIO pins for toggling the LED
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void hardware_init(void)
{
uint32_t ui32Period;
//Set CPU Clock to 40MHz. 400MHz PLL/2 = 200 DIV 5 = 40MHz
SysCtlClockSet(SYSCTL_SYSDIV_5|SYSCTL_USE_PLL|SYSCTL_XTAL_16MHZ|SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN);
// ADD Tiva-C GPIO setup - enables port, sets pins 1-3 (RGB) pins for output
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOF);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1|GPIO_PIN_2|GPIO_PIN_3);
// Turn on the LED
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1|GPIO_PIN_2|GPIO_PIN_3, 4);
// Timer 2 setup code
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_TIMER2); // enable Timer 2 periph clks
TimerConfigure(TIMER2_BASE, TIMER_CFG_PERIODIC); // cfg Timer 2 mode - periodic
ui32Period = (SysCtlClockGet() /2); // period = CPU clk div 2 (500ms)
TimerLoadSet(TIMER2_BASE, TIMER_A, ui32Period); // set Timer 2 period
TimerIntEnable(TIMER2_BASE, TIMER_TIMA_TIMEOUT); // enables Timer 2 to interrupt CPU
TimerEnable(TIMER2_BASE, TIMER_A); // enable Timer 2
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ledToggle()
//
// toggles LED on Tiva-C LaunchPad
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void ledToggle(void)
{
TimerIntClear(TIMER2_BASE, TIMER_TIMA_TIMEOUT); // must clear timer flag FROM timer
// LED values - 2=RED, 4=BLUE, 8=GREEN
if(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2))
{
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1|GPIO_PIN_2|GPIO_PIN_3, 0);
}
else
{
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 4);
}
i16ToggleCount += 1; // keep track of #toggles
Log_info1("LED TOGGLED [%u] TIMES",i16ToggleCount); // send toggle count to UIA
}