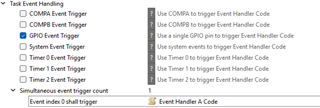
工具/软件:
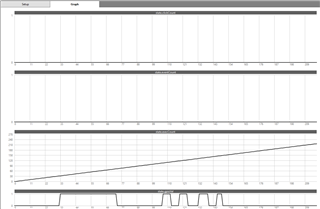
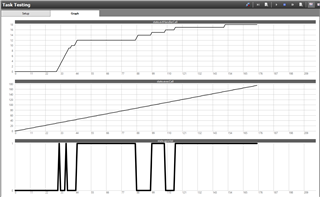
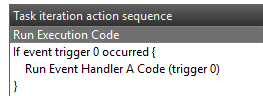
This image shows the task testing. We can see the GPIO is being manually pushed high and low. This is being detected in the execution code. We have an execution counter that we can see is rising. We have an event counter that remains at 0.
This means the event handler code is never being run. This proves that we have the right GPIO line because execution code is able to detect it changing.
Task testing sequence:
Initialisation code:state.clickCount = 0;
state.inClickTrain = 0;
// Set up the first interrupt trigger
evhSetupGpioTrigger(0, AUXIO_I_CLICK_IN, 1, EVH_GPIO_TRIG_ON_EDGE);
// Schedule the next execution
fwScheduleTask(1);
执行代码:
// For debug: copy the GPIO value to a state variable.
gpioGetInputValue(AUXIO_I_CLICK_IN; state.gpioVal);
// For debug: keep a running count of how many times the execution code has run.
state.execCount += 1;
/***** other logic ******/
// Schedule the next execution.
fwScheduleTask(1);
EventHandlerA 代码:
state.eventCount += 1;
// Set up the next interrupt trigger
evhSetupGpioTrigger(0, AUXIO_I_CLICK_IN, 1, EVH_GPIO_TRIG_ON_EDGE);