您好!
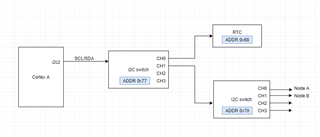
在我们的应用中、我们有一个地址为0x77的 TCA9546A 连接到运行 Ubuntu 的 Cortex A 的内核 i2c2。 我们能够探测连接到开关0x77通道0的器件。 在通道1上、我们有另一个具有 addr 0x70的 i2c 开关。 我们在使用 addr 0x70探测交换机时遇到问题。 我想知道您是否有与多层 i2c 开关的器件树实现相关的文档或支持、如我们的案例所示。
谢谢、
Nikhil
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
您好!
在我们的应用中、我们有一个地址为0x77的 TCA9546A 连接到运行 Ubuntu 的 Cortex A 的内核 i2c2。 我们能够探测连接到开关0x77通道0的器件。 在通道1上、我们有另一个具有 addr 0x70的 i2c 开关。 我们在使用 addr 0x70探测交换机时遇到问题。 我想知道您是否有与多层 i2c 开关的器件树实现相关的文档或支持、如我们的案例所示。

谢谢、
Nikhil
在 Linux 启动时、i2cmux 驱动程序出现错误: "pca954x 6-0070:probe failed"。
对于我们的另一个项目、我们有一个直接连接到内核 i2c2的开关0x70 (基本上中间没有开关0x77)、这种情况很好。 您提到的所有三点都是正确的。 只有当我们在中间添加了一个开关时、我们才会面临这一问题。
我想知道我的器件树结构是否不正确。 对于第二个交换机、我像对第一个交换机那样使用常规寻址。
您认为我必须使用两个单元寻址才能访问第二个交换机节点吗? 基本上类似于以下内容:
多路复用器、77 { #address-cells =<2>; #size-cells =<0>; 兼容="飞利浦、pca9547"; reg =<0x77>; 多路复用器、0.70{ #address-cells =<2>; #size-cells =<0>; 兼容="飞利浦、pca9547"; reg =<0 0x70>; }; 多路复用器、0.71{ #address-cells =<2>; #size-cells =<0>; 兼容="飞利浦、pca9547"; reg =<1 0x71>; };
以上代码不是我的代码、但如果结构正确、我想与您核实一下吗? 您可以在以下链接中找到此内容:
https://lists.ozlabs.org/pipermail/devicetree-discuss/2011-May/005523.html
谢谢、
Nikhil
您好、Nikhil、
我认为这个问题不在本论坛的范围之内。 我非常乐意回答您有关 I2C 器件本身的问题、但我不熟悉如何让 Linux 系统与该器件连接。 我无法就要使用的单元格寻址向您提供建议。 我已通知另一位 I2C 专家有关此主题的信息。 如果他们对此主题有任何了解、他们会告诉我。
我可以在器件树和 Linux 上找到以下一些文档: https://elixir.bootlin.com/linux/v4.9.28/source/Documentation/devicetree/bindings/gpio/gpio.txt
我再次不确定它是否与您的问题有关、因为我不熟悉 Linux 设备树。 如果您在调试器件或测试开关以确保其正常工作方面需要任何帮助、请告诉我。 我一定可以帮助您解决这个问题。
最棒的
Chris
您尚未显示设备树、因此我们无法告诉您它有什么问题。
它可能如下所示:
i2cmux@77 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
compatible = "nxp,pca9546";
reg = <0x77>;
i2c@0 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <0>;
rtc@68 {
compatible = "...";
};
i2cmux@70 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
compatible = "nxp,pca9546";
reg = <0x70>;
i2c@0 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <0>;
...
};
i2c@1 {
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
reg = <1>;
...
};
};
};
};很抱歉、我之前未共享我的设备树。 我正在连接 i2c 多路复用器的器件树实现。 结构语法与您所显示的语法类似。 我仍然无法访问第二个 I2C 开关。 如果您发现我的方法有任何问题、请告诉我。
&i2c2 {
tca9546: i2c2mux9546@77 {
compatible = "nxp,pca9546";
pinctrl-names = "default";
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_i2c2_SWgrp>;
reset-gpios = GP_I2C2_SW_RST;
reg = <0x77>;
status = "okay";
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
//on board peripherals
i2c@0 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
reg = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
rtc@68 {
compatible = "...";
};
};
//Display subsystem
i2c@1 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
reg = <2>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
status = "okay";
Device1@2c {
compatible = "..."
reg = <0x2c>;
status = "disabled";
};
Device2@38 {
compatible = "...";
reg = <0x38>;
};
Device3@5d {
compatible = "...";
pinctrl-names = "default";
reg = <0x5d>;
};
Device4@40 {
compatible = "...";
pinctrl-names = "default";
reg = <0x40>;
};
Device5@41 {
compatible = "...";
reg = <0x41>;
};
Device6@55 {
compatible = "...";
pinctrl-names = "default";
reg = <0x55>;
};
i2cmux9546@70 {
compatible = "pca9546";
reg = <0x70>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
i2c@0 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
reg = <0>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
Device7@48 {
compatible = "..." ;
reg = <0x48> ;
};
};
i2c@1 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
reg = <1>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
};
i2c@2 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
reg = <2>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
};
i2c@3 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
reg = <3>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
Device8@6c {
compatible = "...";
gpio-controller;
reg = <0x6c>;
#gpio-cells = <2>;
};
};
};
};
i2c@3 {
clock-frequency = <100000>;
reg = <3>;
#address-cells = <1>;
#size-cells = <0>;
};
};
};
谢谢