手上有连块280023C芯片板子,一块80PIN脚,一块64PIN脚。把在80PIN芯片上调试好的程序烧到64PIN的芯片里面,can发送会有很多错误帧(CAN引脚是兼容的GPIO4、GPIO5)。
然后就使用例程can_ex1_loopback进行调试,如下过程:
1、配置好引脚、报文信息后,编译烧录。两块板子都能正常发送can报文,无错误帧。
2、将can_ex1_loopback.c中报文数据的赋值语句屏蔽,
// txMsgData[0] = 0x01;
// txMsgData[1] = 0x02;
再测试,80PIN的板子正常发送,但是64PIN的板子会出现错误帧。无法理解屏蔽这两条语句对发送会有什么影响。
这和我再80PIN板子上调好的程序,再64Pin板子上有类似情况。
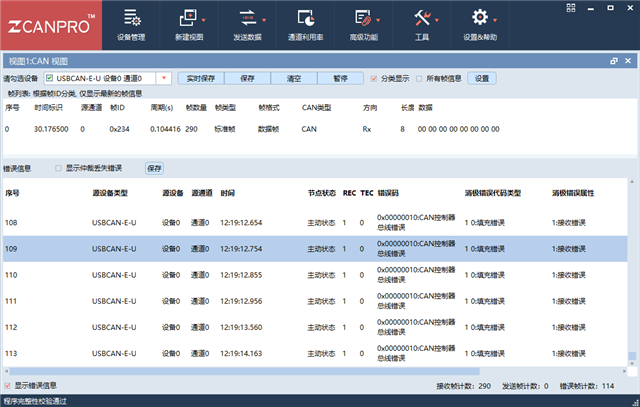
3、对比测试了两块板子芯片端和Can网络上的电压波形,波形的边沿上升下降时间及电平无明显差异。
board.c文件
#include "board.h"
void Board_init()
{
EALLOW;
PinMux_init();
CAN_init();
EDIS;
}
void PinMux_init()
{
//CANA -> myCAN0 Pinmux
GPIO_setPinConfig(GPIO_5_CANA_RX);
GPIO_setPinConfig(GPIO_4_CANA_TX);
}
void CAN_init(){
//myCAN0 initialization
CAN_initModule(myCAN0_BASE);
// Refer to the Driver Library User Guide for information on how to set
// tighter timing control. Additionally, consult the device data sheet
// for more information about the CAN module clocking.
//
CAN_setBitRate(myCAN0_BASE, DEVICE_SYSCLK_FREQ, 250000, 20);
// Initialize the transmit message object used for sending CAN messages.
// Message Object Parameters:
// Message Object ID Number: 1
// Message Identifier: 4660
// Message Frame: CAN_MSG_FRAME_STD
// Message Type: CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX
// Message ID Mask: 0
// Message Object Flags:
// Message Data Length: 8 Bytes
//
CAN_setupMessageObject(myCAN0_BASE, 1, 4660, CAN_MSG_FRAME_STD,CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX, 0, 0,8);
// Initialize the transmit message object used for sending CAN messages.
// Message Object Parameters:
// Message Object ID Number: 2
// Message Identifier: 4660
// Message Frame: CAN_MSG_FRAME_STD
// Message Type: CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX
// Message ID Mask: 0
// Message Object Flags: CAN_MSG_OBJ_NO_FLAGS
// Message Data Length: 8 Bytes
//
CAN_setupMessageObject(myCAN0_BASE, 2, 4660, CAN_MSG_FRAME_STD,CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX, 0, CAN_MSG_OBJ_NO_FLAGS,8);
}
can_ex1_loopback.c文件
#include "driverlib.h"
#include "device.h"
#include "board.h"
//
// Defines
//
#define MSG_DATA_LENGTH 8
//
// Globals
//
volatile unsigned long msgCount = 0;
//
// Main
//
void main(void)
{
uint16_t txMsgData[8], rxMsgData[8];
//
// Initialize device clock and peripherals
//
Device_init();
//
// Initialize GPIO and configure GPIO pins for CANTX/CANRX
//
Device_initGPIO();
//
// Board initialization
//
Board_init();
//
// Initialize PIE and clear PIE registers. Disables CPU interrupts.
//
Interrupt_initModule();
//
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
//
Interrupt_initVectorTable();
//
// Enable Global Interrupt (INTM) and realtime interrupt (DBGM)
//
EINT;
ERTM;
//
// Start CAN module operations
//
CAN_startModule(myCAN0_BASE);
//
// Setup send and receive buffers
//
// txMsgData[0] = 0x01;
// txMsgData[1] = 0x02;
*(uint16_t *)rxMsgData = 0;
//
// Loop Forever - Send and Receive data continuously
//
for(;;)
{
//
// Send CAN message data from message object 1
//
CAN_sendMessage(myCAN0_BASE, 1, MSG_DATA_LENGTH, txMsgData);
//
// Delay before receiving the data
//
DEVICE_DELAY_US(100000);
//
// Read CAN message object 2 and check for new data
//
if (CAN_readMessage(myCAN0_BASE, 2, rxMsgData))
{
//
// Check that received data matches sent data.
// Device will halt here during debug if data doesn't match.
//
if((txMsgData[0] != rxMsgData[0]) ||
(txMsgData[1] != rxMsgData[1]))
{
//asm(" ESTOP0");
}
else
{
//
// Increment message received counter
//
msgCount++;
}
}
else
{
//
// Device will halt here during debug if no new data was received.
//
//asm(" ESTOP0");
}
//
// Increment the value in the transmitted message data.
//
//txMsgData[0] += 0x01;
//txMsgData[1] += 0x01;
//
// Reset data if exceeds a byte
//
if(txMsgData[0] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[0] = 0;
}
if(txMsgData[1] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[1] = 0;
}
}
}
//
// End of File
//
