Other Parts Discussed in Thread: C2000WARE, TMS320F28379D
利用C2000ware中28379D的双核例程led_ex1_blinky_cpu1和led_ex1_blinky_cpu2烧录到开发板上,指示灯可以在CPU1和CPU2的控制下闪烁,之后根据C2000 ware中的单核例程中的can_ex4_simple_transmit中的can例程加入到双核点灯例程中,CAN的GPIO的定义以及CAN的主控选择语句在CPU1中,其他CAN的相应配置在CPU2中定义,在debug过程中CPU2进不去CAN的CAN_initModule(CANB_BASE),暂停CPU2的仿真,出现下面界面。
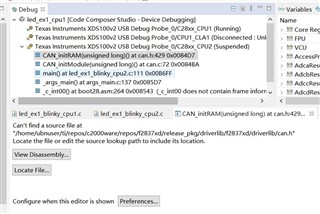
代码如下:
CPU1:
#include "driverlib.h"
#include "device.h"
#include "inc/hw_ipc.h"
void main(void)
{
uint16_t ipcFlag17 = 17U;
Device_init();
Device_initGPIO();
SysCtl_selectCPUForPeripheral(SYSCTL_CPUSEL8_CAN, 2, SYSCTL_CPUSEL_CPU2);
#ifdef _STANDALONE
#ifdef _FLASH
//
// Send boot command to allow the CPU2 application to begin execution
//
Device_bootCPU2(C1C2_BROM_BOOTMODE_BOOT_FROM_FLASH);
#else
//
// Send boot command to allow the CPU2 application to begin execution
//
Device_bootCPU2(C1C2_BROM_BOOTMODE_BOOT_FROM_RAM);
#endif // _FLASH
#endif // _STANDALONE
//
// Initialize GPIO and configure the GPIO pin as a push-pull output
//
GPIO_setPinConfig(GPIO_12_CANTXB);
GPIO_setPinConfig(GPIO_17_CANRXB);
GPIO_setPadConfig(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED1, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
GPIO_setDirectionMode(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED1, GPIO_DIR_MODE_OUT);
GPIO_setPadConfig(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED2, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
GPIO_setDirectionMode(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED2, GPIO_DIR_MODE_OUT);
//
// Configure CPU2 to control the LED GPIO
//
GPIO_setMasterCore(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED2, GPIO_CORE_CPU2);
HWREG(IPC_BASE + IPC_O_SET) = 1UL << ipcFlag17;
//
// Initialize PIE and clear PIE registers. Disables CPU interrupts.
//
Interrupt_initModule();
//
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
//
Interrupt_initVectorTable();
//
// Enable Global Interrupt (INTM) and realtime interrupt (DBGM)
//
EINT;
ERTM;
//
// Loop Forever
//
for(;;)
{
GPIO_writePin(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED1, 0);
DEVICE_DELAY_US(500000);
GPIO_writePin(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED1, 1);
DEVICE_DELAY_US(500000);
}
}
CPU2:
#include "driverlib.h"
#include "device.h"
#include "inc/hw_ipc.h"
//
// Main
//
#define TXCOUNT 100000
#define MSG_DATA_LENGTH 8
#define TX_MSG_OBJ_ID 1
#pragma DATA_SECTION(txMsgData, "SHARERAMGS2");
uint16_t txMsgData[8];
void main(void)
{
uint16_t ipcFlag17 = 17U;
Interrupt_initModule();
//
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
//
Interrupt_initVectorTable();
while(!(HWREG(IPC_BASE + IPC_O_STS) & (1UL << ipcFlag17)))
{
}
//
// ACK IPC flag 17 for CPU1
//
HWREG(IPC_BASE + IPC_O_ACK) = 1UL << ipcFlag17;
CAN_initModule(CANB_BASE);
//
// Set up the CAN bus bit rate to 500kHz for each module
// Refer to the Driver Library User Guide for information on how to set
// tighter timing control. Additionally, consult the device data sheet
// for more information about the CAN module clocking.
//
CAN_setBitRate(CANB_BASE, 200000000, 500000, 20);
//
// Initialize the transmit message object used for sending CAN messages.
// Message Object Parameters:
// CAN Module: A
// Message Object ID Number: 1
// Message Identifier: 0x95555555
// Message Frame: Extended
// Message Type: Transmit
// Message ID Mask: 0x0
// Message Object Flags: None
// Message Data Length: 4 Bytes
//
CAN_setupMessageObject(CANB_BASE, TX_MSG_OBJ_ID, 0x1,
CAN_MSG_FRAME_STD, CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX, 1,
CAN_MSG_OBJ_NO_FLAGS, MSG_DATA_LENGTH);
// Initialize the transmit message object data buffer to be sent
//
txMsgData[0] = 0x01;
txMsgData[1] = 0x23;
txMsgData[2] = 0x45;
txMsgData[3] = 0x67;
txMsgData[4] = 0x89;
txMsgData[5] = 0xAB;
txMsgData[6] = 0xCD;
txMsgData[7] = 0xEF;
//
// Start CAN module A operations
//
CAN_startModule(CANB_BASE);
//
// Enable Global Interrupt (INTM) and realtime interrupt (DBGM)
//
EINT;
ERTM;
//
// Loop Forever
//
for(;;)
{
GPIO_writePin(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED2, 0);
DEVICE_DELAY_US(500000);
GPIO_writePin(DEVICE_GPIO_PIN_LED2, 1);
DEVICE_DELAY_US(500000);
CAN_sendMessage(CANB_BASE, TX_MSG_OBJ_ID, MSG_DATA_LENGTH, txMsgData);
}
}
