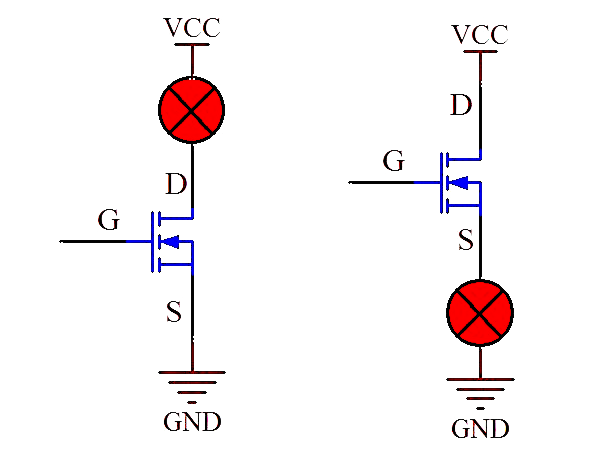
Some people say that NMOS can be used as the upper tube or the lower tube in circuit applications. Which one is better? What is the difference between the two?
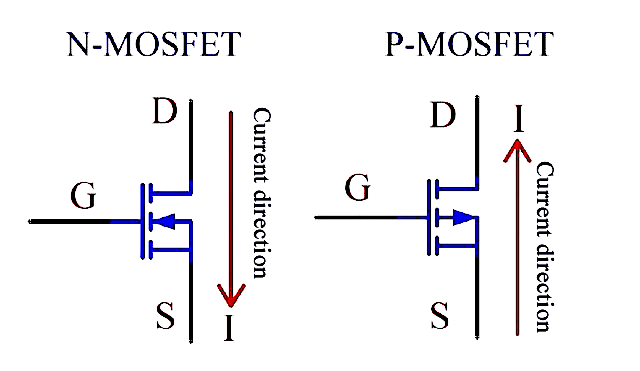
It is known that the current direction of NMOS and PMOS is opposite, and Vgs has a certain voltage difference. However, the G potential of NMOS is higher than the S potential (5~10V), while the S potential of PMOS is higher than the G potential (-5~-10V).
Here, taking the conduction voltage difference of 5V as an example, when NMOS is used as the lower tube, the S pole is directly grounded, and the G pole voltage can be turned on by fixing it to 5V.
NMOS
If NMOS is used as the upper tube, the D pole is connected to the positive power supply, and the voltage of the S pole is not fixed, it is impossible to determine the G pole voltage that controls the conduction of NMOS, because the voltage of the S pole to the ground has two states, the MOS tube is low when it is cut off, and close to the high level VCC when it is turned on. However, when NMOS is used as the upper tube, the control circuit will be more complicated. In this case, an isolated power supply must be used for control. It will be much simpler to use PMOS instead.
PMOS
When using PMOS as the upper tube, the S pole is directly connected to the power supply VCC, the S pole voltage is fixed, and the G pole voltage only needs to be 5V lower than the S pole to conduct; similarly, if PMOS is used as the lower tube, the D pole is grounded, the S pole voltage is not fixed, and the voltage of the control pole G pole cannot be determined, which is more troublesome to use and requires an isolated voltage design.
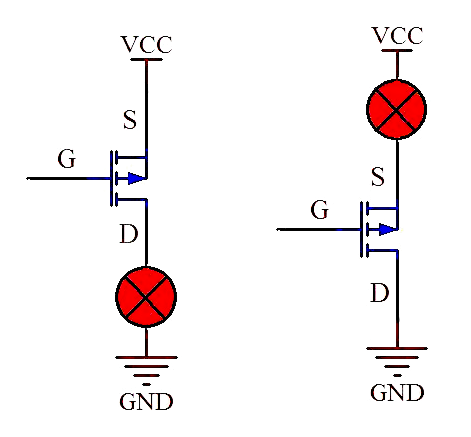
Therefore, PMOS is usually used as the upper tube and NMOS as the lower tube in the circuit.
