主题中讨论的其他器件: DK-TM4C129X
我正在尝试使用 TM4C1290NCZAD 使 UART_Echo 程序在我们的电路板上正常工作。
我从 TI 获得了 UART0的代码。
但我使用的是 UART5。 但它不起作用。
是否有适用于 TM4C1290的任何其他 UART 代码?
谢谢
km
This thread has been locked.
If you have a related question, please click the "Ask a related question" button in the top right corner. The newly created question will be automatically linked to this question.
我正在尝试使用 TM4C1290NCZAD 使 UART_Echo 程序在我们的电路板上正常工作。
我从 TI 获得了 UART0的代码。
但我使用的是 UART5。 但它不起作用。
是否有适用于 TM4C1290的任何其他 UART 代码?
谢谢
km
您好 Kiran、
我想它只是初始化方面的一个小错误、它会一直发生、甚至对我们来说。 您能否发布 UART 代码以便我可以查看它?
此致、
Ralph Jacobi
//*****************************************************************************
//
// uart_echo.c - Example for reading data from and writing data to the UART in
// an interrupt driven fashion.
//
// Copyright (c) 2013-2017 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
// Software License Agreement
//
// Texas Instruments (TI) is supplying this software for use solely and
// exclusively on TI's microcontroller products. The software is owned by
// TI and/or its suppliers, and is protected under applicable copyright
// laws. You may not combine this software with "viral" open-source
// software in order to form a larger program.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND WITH ALL FAULTS.
// NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT
// NOT LIMITED TO, IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE APPLY TO THIS SOFTWARE. TI SHALL NOT, UNDER ANY
// CIRCUMSTANCES, BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
// DAMAGES, FOR ANY REASON WHATSOEVER.
//
// This is part of revision 2.1.4.178 of the DK-TM4C129X Firmware Package.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "driverlib/rom.h"
#include "driverlib/rom_map.h"
#include "grlib/grlib.h"
#include "drivers/kentec320x240x16_ssd2119.h"
#include "drivers/frame.h"
#include "drivers/pinout.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup example_list
//! <h1>UART Echo (uart_echo)</h1>
//!
//! This example application utilizes the UART to echo text. The first UART
//! (connected to the FTDI virtual serial port on the evaluation board) will be
//! configured in 115,200 baud, 8-n-1 mode. All characters received on the
//! UART are transmitted back to the UART.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The error routine that is called if the driver library encounters an error.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
}
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The UART interrupt handler.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
UARTIntHandler(void)
{
uint32_t ui32Status;
//
// Get the interrrupt status.
//
ui32Status = ROM_UARTIntStatus(UART5_BASE, true);
//
// Clear the asserted interrupts.
//
ROM_UARTIntClear(UART5_BASE, ui32Status);
//
// Loop while there are characters in the receive FIFO.
//
while(ROM_UARTCharsAvail(UART5_BASE))
{
//
// Read the next character from the UART and write it back to the UART.
//
ROM_UARTCharPutNonBlocking(UART5_BASE,
UARTCharGetNonBlocking(UART5_BASE));
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Send a string to the UART.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
UARTSend(const uint8_t *pui8Buffer, uint32_t ui32Count)
{
//
// Loop while there are more characters to send.
//
while(ui32Count--)
{
//
// Write the next character to the UART.
//
ROM_UARTCharPutNonBlocking(UART5_BASE, *pui8Buffer++);
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This example demonstrates how to send a string of data to the UART.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
uint32_t ui32SysClock;
tContext sContext;
//
// Run from the PLL at 120 MHz.
//
ui32SysClock = MAP_SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL |
SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
//
// Configure the device pins.
//
PinoutSet();
//
// Initialize the display driver.
//
Kentec320x240x16_SSD2119Init(ui32SysClock);
//
// Initialize the graphics context.
//
GrContextInit(&sContext, &g_sKentec320x240x16_SSD2119);
//
// Draw the application frame.
//
FrameDraw(&sContext, "uart-echo");
//
// Display UART configuration on the display.
//
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Port:", -1, 70, 70, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Baud:", -1, 70, 95, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Data:", -1, 70, 120, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Parity:", -1, 70, 145, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Stop:", -1, 70, 170, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Uart 5", -1, 150, 70, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "115,200 bps", -1, 150, 95, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "8 Bit", -1, 150, 120, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "None", -1, 150, 145, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "1 Bit", -1, 150, 170, 0);
//
// Enable the (non-GPIO) peripherals used by this example. PinoutSet()
// already enabled GPIO Port A.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART5);
//
// Enable processor interrupts.
//
IntMasterEnable();
//
// Configure the UART for 115,200, 8-N-1 operation.
//
ROM_UARTConfigSetExpClk(UART5_BASE, ui32SysClock, 115200,
(UART_CONFIG_WLEN_8 | UART_CONFIG_STOP_ONE |
UART_CONFIG_PAR_NONE));
//
// Enable the UART interrupt.
//
ROM_IntEnable(INT_UART5);
ROM_UARTIntEnable(UART5_BASE, UART_INT_RX | UART_INT_RT);
//
// Prompt for text to be entered.
//
UARTSend((uint8_t *)"Enter text: ", 12);
//
// Loop forever echoing data through the UART.
//
while(1)
{
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// pinout.c - Function to configure the device pins on the DK-TM4C129X.
//
// Copyright (c) 2013-2017 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
// Software License Agreement
//
// Texas Instruments (TI) is supplying this software for use solely and
// exclusively on TI's microcontroller products. The software is owned by
// TI and/or its suppliers, and is protected under applicable copyright
// laws. You may not combine this software with "viral" open-source
// software in order to form a larger program.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND WITH ALL FAULTS.
// NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT
// NOT LIMITED TO, IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE APPLY TO THIS SOFTWARE. TI SHALL NOT, UNDER ANY
// CIRCUMSTANCES, BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
// DAMAGES, FOR ANY REASON WHATSOEVER.
//
// This is part of revision 2.1.4.178 of the DK-TM4C129X Firmware Package.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "inc/hw_gpio.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/rom.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "drivers/pinout.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup pinout_api
//! @{
//
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! Configures the device pins for the standard usages on the DK-TM4C129X.
//!
//! This function enables the GPIO modules and configures the device pins for
//! the default, standard usages on the DK-TM4C129X. Applications that require
//! alternate configurations of the device pins can either not call this
//! function and take full responsibility for configuring all the device pins,
//! or can reconfigure the required device pins after calling this function.
//!
//! \return None.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
PinoutSet(void)
{
//
// Enable all the GPIO peripherals.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOC);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOD);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOE);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOF);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOG);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOH);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOJ);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOK);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOL);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOM);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPION);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOP);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOQ);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOR);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOS);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOT);
//
// PA0-1 are used for UART0.
//
// ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
// ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
// ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// PC6/PH7 are used for UART5.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PC6_U5RX);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PH7_U5TX);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTC_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
//
// PA2-5 are used for SSI0 to the second booster pack.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA2_SSI0CLK);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA3_SSI0FSS);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA4_SSI0XDAT0);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA5_SSI0XDAT1);
//
// PB0-1/PD6-7/PL6-7 are used for USB.
//
HWREG(GPIO_PORTD_BASE + GPIO_O_LOCK) = GPIO_LOCK_KEY;
HWREG(GPIO_PORTD_BASE + GPIO_O_CR) = 0xff;
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PD6_USB0EPEN);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PD7_USB0PFLT);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBAnalog(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBDigital(GPIO_PORTD_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6 | GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBAnalog(GPIO_PORTL_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6 | GPIO_PIN_7);
//
// PB2/PD4 are used for the speaker output.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB2_T5CCP0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeTimer(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTD_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTD_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, 0);
//
// PB6-7 are used for I2C to the TMP100 and the EM connector.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB6_I2C6SCL);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB7_I2C6SDA);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeI2CSCL(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeI2C(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
//
// PE5/PN3/PP1 are used for the push buttons.
//
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// PE7/PP7/PT2-3 are used for the touch screen.
//
HWREG(GPIO_PORTE_BASE + GPIO_O_LOCK) = GPIO_LOCK_KEY;
HWREG(GPIO_PORTE_BASE + GPIO_O_CR) = 0xff;
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTT_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, 0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, 0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTT_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTT_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3, 0);
//
// PF0/PF4-5/PH4/PQ0-2 are used for the SPI flash (on-board and SD card).
// PH4 selects the SD card and PQ1 selects the on-board SPI flash.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF0_SSI3XDAT1);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF4_SSI3XDAT2);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF5_SSI3XDAT3);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PQ0_SSI3CLK);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PQ2_SSI3XDAT0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_PIN_4);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_2);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// PF1/PK4/PK6 are used for Ethernet LEDs.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF1_EN0LED2);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PK4_EN0LED0);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PK6_EN0LED1);
GPIOPinTypeEthernetLED(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1);
GPIOPinTypeEthernetLED(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
GPIOPinTypeEthernetLED(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
//
// PF6-7/PJ6/PS4-5/PR0-7 are used for the LCD.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF7_LCDDATA02);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PJ6_LCDAC);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR0_LCDCP);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR1_LCDFP);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR2_LCDLP);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR3_LCDDATA03);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR4_LCDDATA00);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR5_LCDDATA01);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR6_LCDDATA04);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR7_LCDDATA05);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PS4_LCDDATA06);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PS5_LCDDATA07);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_PIN_6);
GPIOPinTypeLCD(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
GPIOPinTypeLCD(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
GPIOPinTypeLCD(GPIO_PORTR_BASE,
(GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5 | GPIO_PIN_6 | GPIO_PIN_7));
GPIOPinTypeLCD(GPIO_PORTS_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
//
// PQ7 is used for the user LED.
//
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, 0);
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! Configures the USB pins for ULPI connection to an external USB PHY.
//!
//! This function configures the USB ULPI pins to connect the DK-TM4C129X board
//! to an external USB PHY in ULPI mode. This allows the external PHY to act
//! as an external high-speed phy for the DK-TM4C129X. This function must be
//! called after the call to PinoutSet() to properly configure the pins.
//!
//! \return None.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef USE_ULPI
void
USBULPIPinoutSet(void)
{
//
// Enable all the peripherals that are used by the ULPI interface.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOL);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOM);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOP);
//
// ULPI Port B pins.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB2_USB0STP);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB3_USB0CLK);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBDigital(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3,
GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
//
// ULPI Port P pins.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PP2_USB0NXT);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PP3_USB0DIR);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PP4_USB0D7);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PP5_USB0D6);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBDigital(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTP_BASE,
GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 | GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5,
GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
//
// ULPI Port L pins.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL5_USB0D5);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL4_USB0D4);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL3_USB0D3);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL2_USB0D2);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL1_USB0D1);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL0_USB0D0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBDigital(GPIO_PORTL_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1 |
GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTL_BASE,
GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5,
GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
//
// ULPI Port M pins used to control the external USB oscillator and the
// external USB phy on the DK-TM4C129X-DPHY board.
//
// PM1 - Enables the USB oscillator on the DK-TM4C129X-DPHY board.
// PM3 - Enables the USB phy on the DK-TM4C129X-DPHY board.
//
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_3);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_1 |
GPIO_PIN_3);
}
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Close the Doxygen group.
//! @}
//
//*****************************************************************************
您好、Ralph、
我更改了以下两行
IntDefaultHandler、 // UART0 Rx 和 Tx
UARTIntHandler、 // UART5 Rx 和 Tx
但我在 MCU 的 TX 线上看不到任何东西。
我出了什么问题?
即使我的 Tera Term 没有针对以下代码执行任何操作;
UARTSend (((uint8_t *)"输入文本:"、12);
谢谢
Kiran
您好、Ralph、
我正在使用 FTDI 适配器。 对于 UART5、我使用的是 PC6和 pH7。 由于 BGA 器件、无法访问 PH6。 我们的布里斯班办事处使用了 PC6、我不得不继续使用它。 我使用示波器检查了信号。 当我按下笔记本电脑键盘上的键时、我会在 MCU (PC6)的 RX 引脚上看到一个良好的信号、即 FTDI 适配器的 TX。 但我在 MCU 的 TX 引脚(pH7)上看不到任何东西、即 FTDI 适配器的 RX。
这是一个非常简单的电路板。 它具有 CAN 总线、UART、5个输入开关、3个 LED 和一个12V 至3.3V 直流/直流转换器。 除 UART 外、电路板上的所有器件均正常工作。
谢谢
Kiran
这里是我测试开关和 LED 的另一个程序。
//*****************************************************************************
//
// blinky.c - Simple example to blink the on-board LED.
//
// Copyright (c) 2013-2020 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
// Software License Agreement
//
// Texas Instruments (TI) is supplying this software for use solely and
// exclusively on TI's microcontroller products. The software is owned by
// TI and/or its suppliers, and is protected under applicable copyright
// laws. You may not combine this software with "viral" open-source
// software in order to form a larger program.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND WITH ALL FAULTS.
// NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT
// NOT LIMITED TO, IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE APPLY TO THIS SOFTWARE. TI SHALL NOT, UNDER ANY
// CIRCUMSTANCES, BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
// DAMAGES, FOR ANY REASON WHATSOEVER.
//
// This is part of revision 2.2.0.295 of the DK-TM4C129X Firmware Package.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup example_list
//! <h1>Blinky (blinky)</h1>
//!
//! A very simple example that blinks the on-board LED.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The error routine that is called if the driver library encounters an error.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
while(1);
}
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Blink the on-board LED.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
volatile uint32_t ui32Loop;
//
// Enable the GPIO port that is used for the on-board LED.
//
// SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOQ);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOM);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOJ);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOH);
SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOC);
//
// Check if the peripheral access is enabled.
//
// while(!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOQ))
while(!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOM))
{
}
while(!SysCtlPeripheralReady(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOJ))
{
}
//
// Enable the GPIO pin for the LED (PQ7). Set the direction as output, and
// enable the GPIO pin for digital function.
//
// GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0); //LED-GRN
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1); //LED-RED
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2); //LED-AUTO
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2); //SWITCH-AUTO
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3); //SWITCH-INC
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4); //SWITCH-DEC
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6); //SWITCH-FUNCTION
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7); //SWITCH-MATCH
GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7); //UART-TX
GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTC_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6); //UART-RX
int S1_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2))); // True if PJ.2 low (button pressed)
int S2_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3))); // True if PJ.3 low (button pressed)
int S3_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4))); // True if PJ.4 low (button pressed)
int S4_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6))); // True if PJ.6 low (button pressed)
int S5_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7))); // True if PJ.7 low (button pressed)
int SRx_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTC_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6))); // True if RX low (button pressed)
// Loop forever.
//
while(1)
{
//
// Turn on the LED.
//
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, GPIO_PIN_7);
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_0); //LED-GRN ON
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_1); //LED-RED ON
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, 0x0); //LED-GRN OFF
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_2); //LED-AUTO OFF
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, GPIO_PIN_7); //UART-TX OFF
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTC_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_PIN_6); //UART-RX OFF
//
// Delay for a bit.
//
int S1_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2))); // True if PJ.2 low (button pressed)
int S2_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3))); // True if PJ.3 low (button pressed)
int S3_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4))); // True if PJ.4 low (button pressed)
int S4_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6))); // True if PJ.6 low (button pressed)
int S5_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7))); // True if PJ.7 low (button pressed)
int SRx_pressed = (!(GPIOPinRead(GPIO_PORTC_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6))); // True if RX low (button pressed)
if (S1_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 1340000; ui32Loop++) // 1 second ON
{
}
}
else if (S2_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 2680000; ui32Loop++) // 2 second ON
{
}
}
else if (S3_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 4020000; ui32Loop++) // 3 second ON
{
}
}
else if (S4_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 5360000; ui32Loop++) // 4 second ON
{
}
}
else if (S5_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 6700000; ui32Loop++) // 5 second ON
{
}
}
else if (SRx_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 350000; ui32Loop++) // 5 second ON
{
}
}
else
{
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 670000; ui32Loop++) // 0.5 second ON
{
}
}
//
// Turn off the LED.
//
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, 0x0);
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, 0x0); //LED-GRN OFF
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, 0x0); //LED-RED OFF
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_0); //LED-GRN ON
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2, 0x0); //LED-AUTO ON
GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, 0x0); //UART-TX ON
// GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTC_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6, 0x0); //UART-RX ON
//
// Delay for a bit.
//
if (S1_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 1340000; ui32Loop++) // 1 second ON
{
}
}
else if (S2_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 2680000; ui32Loop++) // 2 second ON
{
}
}
else if (S3_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 4020000; ui32Loop++) // 3 second ON
{
}
}
else if (S4_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 5360000; ui32Loop++) // 4 second ON
{
}
}
else if (S5_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 6700000; ui32Loop++) // 5 second ON
{
}
}
else if (SRx_pressed){
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 350000; ui32Loop++) // 5 second ON
{
}
}
else
{
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 670000; ui32Loop++) // 0.5 second ON
{
}
}
}
}
您好 Kiran、
您是否在连接了 FTDI 的情况下运行了该项目并看到了当时的切换? 表明 FTDI 不会导致任何问题。
当配置为 GPIO 时、I/O 切换很好、但它仍然不能真正解释为什么 UART 不能正常工作。
我现在唯一能想到的另一件事是:
不确定您是否有第二个 FTDI、您只需进行完整性检查即可进行测试。
此致、
Ralph Jacobi
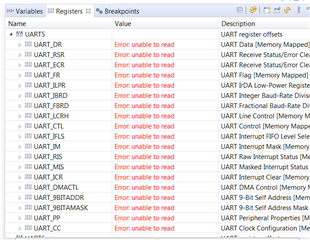
您好、Ralph、
根据您的建议、我在 while 循环中添加了一个断点。
但 UART5寄存器显示启用读取。 有什么想法吗?
我得到以下结果。 还插入了我更改的3个文件。
谢谢
Kiran
//*****************************************************************************
//
// uart_echo.c - Example for reading data from and writing data to the UART in
// an interrupt driven fashion.
//
// Copyright (c) 2013-2017 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
// Software License Agreement
//
// Texas Instruments (TI) is supplying this software for use solely and
// exclusively on TI's microcontroller products. The software is owned by
// TI and/or its suppliers, and is protected under applicable copyright
// laws. You may not combine this software with "viral" open-source
// software in order to form a larger program.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND WITH ALL FAULTS.
// NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT
// NOT LIMITED TO, IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE APPLY TO THIS SOFTWARE. TI SHALL NOT, UNDER ANY
// CIRCUMSTANCES, BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
// DAMAGES, FOR ANY REASON WHATSOEVER.
//
// This is part of revision 2.1.4.178 of the DK-TM4C129X Firmware Package.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "inc/hw_ints.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/debug.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/interrupt.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "driverlib/uart.h"
#include "driverlib/rom.h"
#include "driverlib/rom_map.h"
#include "grlib/grlib.h"
#include "drivers/kentec320x240x16_ssd2119.h"
#include "drivers/frame.h"
#include "drivers/pinout.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup example_list
//! <h1>UART Echo (uart_echo)</h1>
//!
//! This example application utilizes the UART to echo text. The first UART
//! (connected to the FTDI virtual serial port on the evaluation board) will be
//! configured in 115,200 baud, 8-n-1 mode. All characters received on the
//! UART are transmitted back to the UART.
//
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The error routine that is called if the driver library encounters an error.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef DEBUG
void
__error__(char *pcFilename, uint32_t ui32Line)
{
}
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The UART interrupt handler.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
UARTIntHandler(void)
{
uint32_t ui32Status;
//
// Get the interrrupt status.
//
ui32Status = ROM_UARTIntStatus(UART5_BASE, true);
//
// Clear the asserted interrupts.
//
ROM_UARTIntClear(UART5_BASE, ui32Status);
//
// Loop while there are characters in the receive FIFO.
//
while(ROM_UARTCharsAvail(UART5_BASE))
{
//
// Read the next character from the UART and write it back to the UART.
//
ROM_UARTCharPutNonBlocking(UART5_BASE,
UARTCharGetNonBlocking(UART5_BASE));
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Send a string to the UART.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
UARTSend(const uint8_t *pui8Buffer, uint32_t ui32Count)
{
//
// Loop while there are more characters to send.
//
while(ui32Count--)
{
//
// Write the next character to the UART.
//
ROM_UARTCharPutNonBlocking(UART5_BASE, *pui8Buffer++);
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This example demonstrates how to send a string of data to the UART.
//
//*****************************************************************************
int
main(void)
{
volatile uint32_t ui32Loop;
uint32_t ui32SysClock;
tContext sContext;
//
// Run from the PLL at 120 MHz.
//
ui32SysClock = MAP_SysCtlClockFreqSet((SYSCTL_XTAL_25MHZ |
SYSCTL_OSC_MAIN | SYSCTL_USE_PLL |
SYSCTL_CFG_VCO_480), 120000000);
//
// Configure the device pins.
//
PinoutSet();
//
// Initialize the display driver.
//
Kentec320x240x16_SSD2119Init(ui32SysClock);
//
// Initialize the graphics context.
//
GrContextInit(&sContext, &g_sKentec320x240x16_SSD2119);
//
// Draw the application frame.
//
FrameDraw(&sContext, "uart-echo");
//
// Display UART configuration on the display.
//
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Port:", -1, 70, 70, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Baud:", -1, 70, 95, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Data:", -1, 70, 120, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Parity:", -1, 70, 145, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Stop:", -1, 70, 170, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "Uart 5", -1, 150, 70, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "115,200 bps", -1, 150, 95, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "8 Bit", -1, 150, 120, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "None", -1, 150, 145, 0);
GrStringDraw(&sContext, "1 Bit", -1, 150, 170, 0);
//
// Enable the (non-GPIO) peripherals used by this example. PinoutSet()
// already enabled GPIO Port A.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_UART5);
//
// Enable processor interrupts.
//
IntMasterEnable();
//
// Configure the UART for 115,200, 8-N-1 operation.
//
ROM_UARTConfigSetExpClk(UART5_BASE, ui32SysClock, 115200,
(UART_CONFIG_WLEN_8 | UART_CONFIG_STOP_ONE |
UART_CONFIG_PAR_NONE));
//
// Enable the UART interrupt.
//
ROM_IntEnable(INT_UART5);
ROM_UARTIntEnable(UART5_BASE, UART_INT_RX | UART_INT_RT);
//
// Prompt for text to be entered.
//
UARTSend((uint8_t *)"Enter text: ", 12);
//
// Loop forever echoing data through the UART.
//
while(1)
{
UARTSend((uint8_t *)"Enter text: ", 12);
for(ui32Loop = 0; ui32Loop < 1340000; ui32Loop++) // 1 second ON
{
}
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// pinout.c - Function to configure the device pins on the DK-TM4C129X.
//
// Copyright (c) 2013-2017 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
// Software License Agreement
//
// Texas Instruments (TI) is supplying this software for use solely and
// exclusively on TI's microcontroller products. The software is owned by
// TI and/or its suppliers, and is protected under applicable copyright
// laws. You may not combine this software with "viral" open-source
// software in order to form a larger program.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND WITH ALL FAULTS.
// NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT
// NOT LIMITED TO, IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE APPLY TO THIS SOFTWARE. TI SHALL NOT, UNDER ANY
// CIRCUMSTANCES, BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
// DAMAGES, FOR ANY REASON WHATSOEVER.
//
// This is part of revision 2.1.4.178 of the DK-TM4C129X Firmware Package.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "inc/hw_gpio.h"
#include "inc/hw_memmap.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
#include "driverlib/gpio.h"
#include "driverlib/pin_map.h"
#include "driverlib/rom.h"
#include "driverlib/sysctl.h"
#include "drivers/pinout.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! \addtogroup pinout_api
//! @{
//
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! Configures the device pins for the standard usages on the DK-TM4C129X.
//!
//! This function enables the GPIO modules and configures the device pins for
//! the default, standard usages on the DK-TM4C129X. Applications that require
//! alternate configurations of the device pins can either not call this
//! function and take full responsibility for configuring all the device pins,
//! or can reconfigure the required device pins after calling this function.
//!
//! \return None.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
PinoutSet(void)
{
//
// Enable all the GPIO peripherals.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOA);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOC);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOD);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOE);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOF);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOG);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOH);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOJ);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOK);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOL);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOM);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPION);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOP);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOQ);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOR);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOS);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOT);
//
// PA0-1 are used for UART0.
//
// ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA0_U0RX);
// ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA1_U0TX);
// ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTA_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// PB0-1 are used for UART1.
//
// ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB0_U1RX);
// ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB1_U1TX);
// ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// PC6/PH7 are used for UART5.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PC6_U5RX);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PH7_U5TX);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTC_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUART(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
//
// PA2-5 are used for SSI0 to the second booster pack.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA2_SSI0CLK);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA3_SSI0FSS);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA4_SSI0XDAT0);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PA5_SSI0XDAT1);
//
// PB0-1/PD6-7/PL6-7 are used for USB.
//
HWREG(GPIO_PORTD_BASE + GPIO_O_LOCK) = GPIO_LOCK_KEY;
HWREG(GPIO_PORTD_BASE + GPIO_O_CR) = 0xff;
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PD6_USB0EPEN);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PD7_USB0PFLT);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBAnalog(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBDigital(GPIO_PORTD_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6 | GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBAnalog(GPIO_PORTL_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6 | GPIO_PIN_7);
//
// PB2/PD4 are used for the speaker output.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB2_T5CCP0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeTimer(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTD_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTD_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, 0);
//
// PB6-7 are used for I2C to the TMP100 and the EM connector.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB6_I2C6SCL);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB7_I2C6SDA);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeI2CSCL(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeI2C(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
//
// PE5/PN3/PP1 are used for the push buttons.
//
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_5);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTN_BASE, GPIO_PIN_3);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// PE7/PP7/PT2-3 are used for the touch screen.
//
HWREG(GPIO_PORTE_BASE + GPIO_O_LOCK) = GPIO_LOCK_KEY;
HWREG(GPIO_PORTE_BASE + GPIO_O_CR) = 0xff;
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOInput(GPIO_PORTT_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTE_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, 0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, 0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTT_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTT_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3, 0);
//
// PF0/PF4-5/PH4/PQ0-2 are used for the SPI flash (on-board and SD card).
// PH4 selects the SD card and PQ1 selects the on-board SPI flash.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF0_SSI3XDAT1);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF4_SSI3XDAT2);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF5_SSI3XDAT3);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PQ0_SSI3CLK);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PQ2_SSI3XDAT0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTH_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4, GPIO_PIN_4);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeSSI(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_2);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_1);
//
// PF1/PK4/PK6 are used for Ethernet LEDs.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF1_EN0LED2);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PK4_EN0LED0);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PK6_EN0LED1);
GPIOPinTypeEthernetLED(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1);
GPIOPinTypeEthernetLED(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4);
GPIOPinTypeEthernetLED(GPIO_PORTK_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
//
// PF6-7/PJ6/PS4-5/PR0-7 are used for the LCD.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PF7_LCDDATA02);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PJ6_LCDAC);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR0_LCDCP);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR1_LCDFP);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR2_LCDLP);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR3_LCDDATA03);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR4_LCDDATA00);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR5_LCDDATA01);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR6_LCDDATA04);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PR7_LCDDATA05);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PS4_LCDDATA06);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PS5_LCDDATA07);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6, GPIO_PIN_6);
GPIOPinTypeLCD(GPIO_PORTF_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
GPIOPinTypeLCD(GPIO_PORTJ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_6);
GPIOPinTypeLCD(GPIO_PORTR_BASE,
(GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5 | GPIO_PIN_6 | GPIO_PIN_7));
GPIOPinTypeLCD(GPIO_PORTS_BASE, GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
//
// PQ7 is used for the user LED.
//
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTQ_BASE, GPIO_PIN_7, 0);
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
//! Configures the USB pins for ULPI connection to an external USB PHY.
//!
//! This function configures the USB ULPI pins to connect the DK-TM4C129X board
//! to an external USB PHY in ULPI mode. This allows the external PHY to act
//! as an external high-speed phy for the DK-TM4C129X. This function must be
//! called after the call to PinoutSet() to properly configure the pins.
//!
//! \return None.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#ifdef USE_ULPI
void
USBULPIPinoutSet(void)
{
//
// Enable all the peripherals that are used by the ULPI interface.
//
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOB);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOL);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOM);
ROM_SysCtlPeripheralEnable(SYSCTL_PERIPH_GPIOP);
//
// ULPI Port B pins.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB2_USB0STP);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PB3_USB0CLK);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBDigital(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTB_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3,
GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
//
// ULPI Port P pins.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PP2_USB0NXT);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PP3_USB0DIR);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PP4_USB0D7);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PP5_USB0D6);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBDigital(GPIO_PORTP_BASE, GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTP_BASE,
GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 | GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5,
GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
//
// ULPI Port L pins.
//
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL5_USB0D5);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL4_USB0D4);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL3_USB0D3);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL2_USB0D2);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL1_USB0D1);
ROM_GPIOPinConfigure(GPIO_PL0_USB0D0);
ROM_GPIOPinTypeUSBDigital(GPIO_PORTL_BASE, GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1 |
GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5);
GPIOPadConfigSet(GPIO_PORTL_BASE,
GPIO_PIN_0 | GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_2 | GPIO_PIN_3 |
GPIO_PIN_4 | GPIO_PIN_5,
GPIO_STRENGTH_12MA, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);
//
// ULPI Port M pins used to control the external USB oscillator and the
// external USB phy on the DK-TM4C129X-DPHY board.
//
// PM1 - Enables the USB oscillator on the DK-TM4C129X-DPHY board.
// PM3 - Enables the USB phy on the DK-TM4C129X-DPHY board.
//
ROM_GPIOPinTypeGPIOOutput(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_3);
ROM_GPIOPinWrite(GPIO_PORTM_BASE, GPIO_PIN_1 | GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_1 |
GPIO_PIN_3);
}
#endif
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Close the Doxygen group.
//! @}
//
//*****************************************************************************
//*****************************************************************************
//
// startup_ccs.c - Startup code for use with TI's Code Composer Studio.
//
// Copyright (c) 2013-2017 Texas Instruments Incorporated. All rights reserved.
// Software License Agreement
//
// Texas Instruments (TI) is supplying this software for use solely and
// exclusively on TI's microcontroller products. The software is owned by
// TI and/or its suppliers, and is protected under applicable copyright
// laws. You may not combine this software with "viral" open-source
// software in order to form a larger program.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND WITH ALL FAULTS.
// NO WARRANTIES, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT
// NOT LIMITED TO, IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE APPLY TO THIS SOFTWARE. TI SHALL NOT, UNDER ANY
// CIRCUMSTANCES, BE LIABLE FOR SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
// DAMAGES, FOR ANY REASON WHATSOEVER.
//
// This is part of revision 2.1.4.178 of the DK-TM4C129X Firmware Package.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#include <stdint.h>
#include "inc/hw_nvic.h"
#include "inc/hw_types.h"
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Forward declaration of the default fault handlers.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void ResetISR(void);
static void NmiSR(void);
static void FaultISR(void);
static void IntDefaultHandler(void);
//*****************************************************************************
//
// External declaration for the reset handler that is to be called when the
// processor is started
//
//*****************************************************************************
extern void _c_int00(void);
//*****************************************************************************
//
// Linker variable that marks the top of the stack.
//
//*****************************************************************************
extern uint32_t __STACK_TOP;
//*****************************************************************************
//
// External declaration for the interrupt handler used by the application.
//
//*****************************************************************************
extern void UARTIntHandler(void);
//*****************************************************************************
//
// The vector table. Note that the proper constructs must be placed on this to
// ensure that it ends up at physical address 0x0000.0000 or at the start of
// the program if located at a start address other than 0.
//
//*****************************************************************************
#pragma DATA_SECTION(g_pfnVectors, ".intvecs")
void (* const g_pfnVectors[])(void) =
{
(void (*)(void))((uint32_t)&__STACK_TOP),
// The initial stack pointer
ResetISR, // The reset handler
NmiSR, // The NMI handler
FaultISR, // The hard fault handler
IntDefaultHandler, // The MPU fault handler
IntDefaultHandler, // The bus fault handler
IntDefaultHandler, // The usage fault handler
0, // Reserved
0, // Reserved
0, // Reserved
0, // Reserved
IntDefaultHandler, // SVCall handler
IntDefaultHandler, // Debug monitor handler
0, // Reserved
IntDefaultHandler, // The PendSV handler
IntDefaultHandler, // The SysTick handler
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port A
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port B
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port C
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port D
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port E
IntDefaultHandler, // UART0 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART1 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // SSI0 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C0 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Fault
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Generator 0
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Generator 1
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Generator 2
IntDefaultHandler, // Quadrature Encoder 0
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC Sequence 0
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC Sequence 1
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC Sequence 2
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC Sequence 3
IntDefaultHandler, // Watchdog timer
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 0 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 0 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 1 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 1 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 2 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 2 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Analog Comparator 0
IntDefaultHandler, // Analog Comparator 1
IntDefaultHandler, // Analog Comparator 2
IntDefaultHandler, // System Control (PLL, OSC, BO)
IntDefaultHandler, // FLASH Control
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port F
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port G
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port H
IntDefaultHandler, // UART2 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // SSI1 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 3 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 3 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C1 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // CAN0
IntDefaultHandler, // CAN1
IntDefaultHandler, // Ethernet
IntDefaultHandler, // Hibernate
IntDefaultHandler, // USB0
IntDefaultHandler, // PWM Generator 3
IntDefaultHandler, // uDMA Software Transfer
IntDefaultHandler, // uDMA Error
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC1 Sequence 0
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC1 Sequence 1
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC1 Sequence 2
IntDefaultHandler, // ADC1 Sequence 3
IntDefaultHandler, // External Bus Interface 0
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port J
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port K
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port L
IntDefaultHandler, // SSI2 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // SSI3 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART3 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART4 Rx and Tx
UARTIntHandler, // UART5 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART6 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // UART7 Rx and Tx
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C2 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C3 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 4 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 4 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 5 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 5 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // FPU
0, // Reserved
0, // Reserved
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C4 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C5 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port M
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port N
0, // Reserved
IntDefaultHandler, // Tamper
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P (Summary or P0)
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P1
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P2
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P3
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P4
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P5
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P6
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port P7
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q (Summary or Q0)
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q1
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q2
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q3
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q4
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q5
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q6
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port Q7
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port R
IntDefaultHandler, // GPIO Port S
IntDefaultHandler, // SHA/MD5 0
IntDefaultHandler, // AES 0
IntDefaultHandler, // DES3DES 0
IntDefaultHandler, // LCD Controller 0
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 6 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 6 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 7 subtimer A
IntDefaultHandler, // Timer 7 subtimer B
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C6 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C7 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // HIM Scan Matrix Keyboard 0
IntDefaultHandler, // One Wire 0
IntDefaultHandler, // HIM PS/2 0
IntDefaultHandler, // HIM LED Sequencer 0
IntDefaultHandler, // HIM Consumer IR 0
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C8 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler, // I2C9 Master and Slave
IntDefaultHandler // GPIO Port T
};
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This is the code that gets called when the processor first starts execution
// following a reset event. Only the absolutely necessary set is performed,
// after which the application supplied entry() routine is called. Any fancy
// actions (such as making decisions based on the reset cause register, and
// resetting the bits in that register) are left solely in the hands of the
// application.
//
//*****************************************************************************
void
ResetISR(void)
{
//
// Jump to the CCS C initialization routine. This will enable the
// floating-point unit as well, so that does not need to be done here.
//
__asm(" .global _c_int00\n"
" b.w _c_int00");
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This is the code that gets called when the processor receives a NMI. This
// simply enters an infinite loop, preserving the system state for examination
// by a debugger.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static void
NmiSR(void)
{
//
// Enter an infinite loop.
//
while(1)
{
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This is the code that gets called when the processor receives a fault
// interrupt. This simply enters an infinite loop, preserving the system state
// for examination by a debugger.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static void
FaultISR(void)
{
//
// Enter an infinite loop.
//
while(1)
{
}
}
//*****************************************************************************
//
// This is the code that gets called when the processor receives an unexpected
// interrupt. This simply enters an infinite loop, preserving the system state
// for examination by a debugger.
//
//*****************************************************************************
static void
IntDefaultHandler(void)
{
//
// Go into an infinite loop.
//
while(1)
{
}
}