主题中讨论的其他器件:C2000WARE
尊敬的团队:
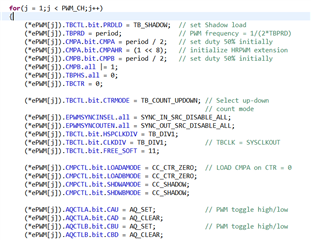
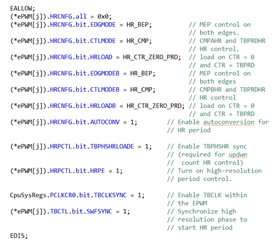
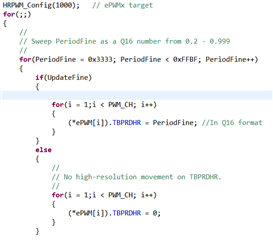
C:\ti\c2000Ware_3_04_00_00\device_support\f28002x\examples\HRPWM\HRPWM_ex2_prdupdown_SFO_v8.c
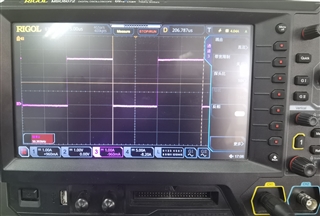
当我的一个客户端测试 HRPWM 例程时、他发现当 HRPWM 的开关频率 为5MHz 时、可以观察到周期性的边沿位置变化。
但是、当 PWM 频率为50kHz 时、在示波器上看不到边沿。
他想知道这是否是因为 HRPWM 对其开关频率有最低要求? 如果没有、为什么50kHz 时没有变化?
此致