在TI提供的库中,几种基本的数据类型的定义如下:
#ifndef DSP28_DATA_TYPES #define DSP28_DATA_TYPES typedef int int16;// = 2? typedef long int32; // = 4? typedef long long int64; // = 8? typedef unsigned int Uint16; // = 2? typedef unsigned long Uint32; // = 4? typedef unsigned long long Uint64; // = 8? typedef float float32; typedef long double float64; #endif
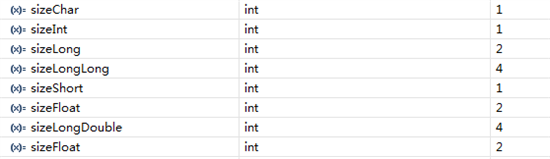
但是,在实际的sizeof代码测试中,返回的值结果并不一样:
使用的代码是:
int sizeChar,sizeShort,sizeInt,sizeLong,sizeLongLong,sizeLongDouble,sizeFloat;
int main(void) {
sizeChar = sizeof(char);
sizeShort = sizeof(short);
sizeInt = sizeof(int);
sizeLong = sizeof(long);
sizeLongLong = sizeof(long long);
sizeFloat = sizeof(float);
sizeLongDouble = sizeof(long double);
return 0;
}
后续,继续测试,使用一个共同体,测试如下:
union u_temp{
Uint32 _int32;
unsigned char _int8[4];
}temp;
int main(void) {
temp._int32 = 0x12345678;
return 0;
}
也就是说,假如char是正常的8位宽度的话,实际标注的Uint32的宽度实际上也仅仅是16位。只有使用到longlong才能提供32位宽度的数据类型。