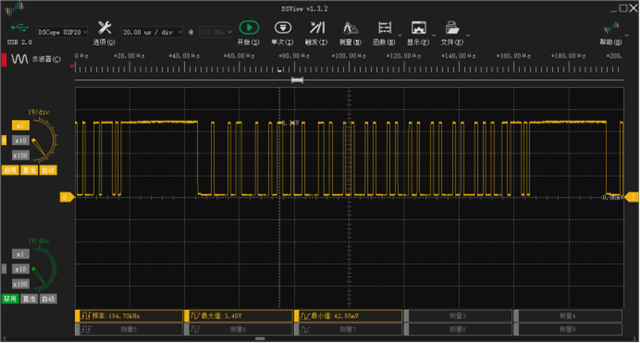
如题,下图是开发板TX与地的波形
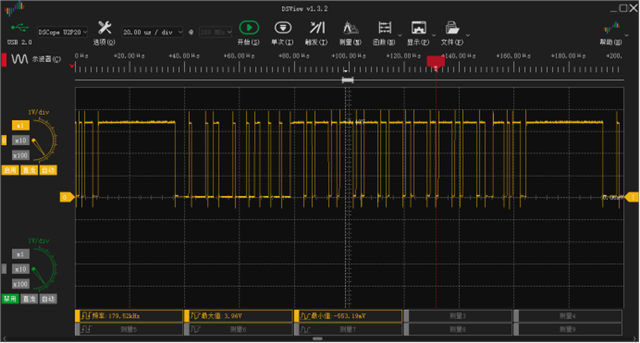
开发板的RX与地
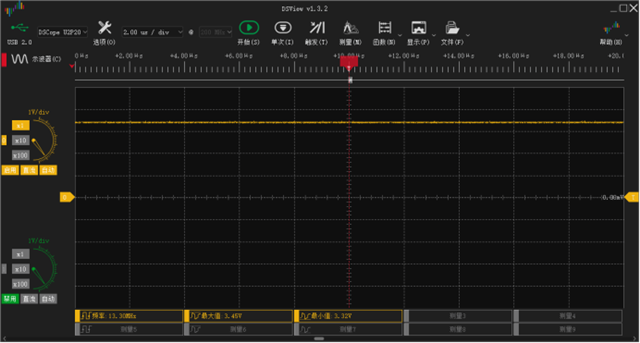
下图为我自己的板子TX与地
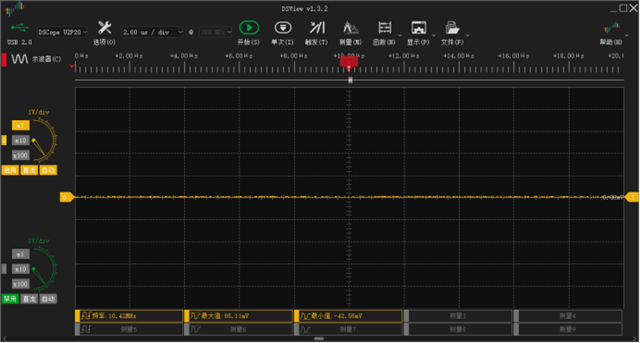
RX与地
下面为代码,上面的是开发板的,下面注释的是我自己板子的,区别仅仅是一个使用CANA一个使用CANB,请问可能是什么原因呢?
//#############################################################################
//
// FILE: can_ex2_loopback_interrupts.c
//
// TITLE: CAN External Loopback with Interrupts Example
//
//! \addtogroup driver_example_list
//! <h1> CAN External Loopback with Interrupts </h1>
//!
/* 这段代码实现了CAN总线的外部回环测试(External Loopback),通过中断机制实现数据的自发自收。主要功能:
初始化CAN模块,配置为外部回环模式(数据从TXpin发出后,内部直接回到RX端:TX->TXpin->RX)。
配置两个消息对象(邮箱):一个用于发送数据(TX),一个用于接收数据(RX)。
每秒发送一次递增数据,通过中断确认发送完成和接收数据。
统计发送和接收的消息数量,并检查错误。
*/
//! This example shows the basic setup of CAN in order to transmit and receive
//! messages on the CAN bus. The CAN peripheral is configured to transmit
//! messages with a specific CAN ID. A message is then transmitted once per
//! second, using a simple delay loop for timing. The message that is sent is
//! a 4 byte message that contains an incrementing pattern. A CAN interrupt
//! handler is used to confirm message transmission and count the number of
//! messages that have been sent.
//!
//! This example sets up the CAN controller in External Loopback test mode.
//! Data transmitted is visible on the CANTXA pin and is received internally
//! back to the CAN Core. CAN-B module is not involved.
//!
//! Note: "External" loopback does not mean the loopback is done externally.
//! The loopback is done internally, but the transmitted data can be seen
//! externally on the CANTX pin.
//!
//! \b External \b Connections \n
//! - None. (Transmitting node generates its own ACK)
//!
//! \b Watch \b Variables \n
//! - txMsgCount - A counter for the number of messages sent
//! - rxMsgCount - A counter for the number of messages received
//! - txMsgData - An array with the data being sent
//! - rxMsgData - An array with the data that was received
//! - errorFlag - A flag that indicates an error has occurred
//!
//
//#############################################################################
//
//
// $Copyright:
// Copyright (C) 2013-2024 Texas Instruments Incorporated - http://www.ti.com/
//
// Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
// modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
// are met:
//
// Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
//
// Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
// notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
// documentation and/or other materials provided with the
// distribution.
//
// Neither the name of Texas Instruments Incorporated nor the names of
// its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
// from this software without specific prior written permission.
//
// THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
// "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
// LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
// A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
// OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
// SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
// LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
// DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
// THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
// (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
// OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
// $
//#############################################################################
//
// Included Files
//
//#include "driverlib.h"
//#include "device.h"
//// 主控为发送数据给开发板,开发板再返回55给主控
//// 此为开发板程序
//// Defines
////
//#define MSG_DATA_LENGTH 8
//#define TX_MSG_OBJ_ID 1
//#define RX_MSG_OBJ_ID 2
//
////
//// Globals
////
//volatile uint32_t txMsgCount = 0;
//volatile uint32_t rxMsgCount = 0;
//volatile uint32_t errorFlag = 0;
//uint32_t ISR_Count = 0;
//uint16_t txMsgData[MSG_DATA_LENGTH];
//uint16_t rxMsgData[MSG_DATA_LENGTH];
//
////
//// Function Prototypes
////
//__interrupt void canISR(void);
//
////
//// Main
////
//void main(void)
//{
// //
// // Initialize device clock and peripherals
// //
// Device_init();
//
// //
// // Initialize GPIO and configure GPIO pins for CANTX/CANRX
// //
// Device_initGPIO();
// GPIO_setPinConfig(DEVICE_GPIO_CFG_CANRXA);
// GPIO_setPinConfig(DEVICE_GPIO_CFG_CANTXA);
//
// //LED收到上位机命令翻转
// GPIO_setMasterCore(133, GPIO_CORE_CPU1);//CPU1控制
// GPIO_setPinConfig(GPIO_133_GPIO133);//配置为普通GPIO
// GPIO_writePin(133,1);
// GPIO_setDirectionMode(133, GPIO_DIR_MODE_OUT);
// GPIO_setPadConfig(133, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);//默认配置,通常表示标准的推挽输出(push-pull output)或悬空输入(floating input)
// //LED发送翻转
// GPIO_setMasterCore(99, GPIO_CORE_CPU1);//CPU1控制
// GPIO_setPinConfig(GPIO_99_GPIO99);//配置为普通GPIO
// GPIO_writePin(99,1);
// GPIO_setDirectionMode(99, GPIO_DIR_MODE_OUT);
// GPIO_setPadConfig(99, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);//默认配置,通常表示标准的推挽输出(push-pull output)或悬空输入(floating input)
//
// //
// // Initialize the CAN controller
// //
// // Puts the module in Initialization mode, Disables the parity function
// // Initializes the MBX RAM, Initiates a S/W reset of the module
// // Seeks write-access to configuration registers.
// // 初始化CAN控制器 将模块置于初始化模式,禁用奇偶校验功能初始化MBX RAM,启动模块的S/W复位寻求对配置寄存器的写访问。
//
// CAN_initModule(CANA_BASE);
//
// //
// // Set up the CAN bus bit rate to 500 kbps
// // Refer to the Driver Library User Guide for information on how to set
// // tighter timing control. Additionally, consult the device data sheet
// // for more information about the CAN module clocking.
// // CAN比特率为500kbps
// // 20为bitTime(时间量子),每个CAN位(Bit)的时间由20个时间量子组成(范围:8-25)
// // 波特率为500k,则发送一位时间=1/500k=2000ns,所以每个bitTime为2000ns/20=100ns
// CAN_setBitRate(CANA_BASE, DEVICE_SYSCLK_FREQ, 1000000, 20);
//
//
// //
// // Enable interrupts on the CAN peripheral.
// // Enables Interrupt line 0, Error & Status Change interrupts in CAN_CTL
// // register.
// // 允许产生中断线0中断(status、error、mb(mb中断允许在RX的CAN_setupMessageObject中:CAN_MSG_OBJ_RX_INT_ENABLE))、错误中断、状态变化中断(控制器状态变化?)
// CAN_enableInterrupt(CANA_BASE, CAN_INT_IE0 | CAN_INT_ERROR |
// CAN_INT_STATUS);
//
// //
// // Initialize PIE and clear PIE registers. Disables CPU interrupts.
// //
// Interrupt_initModule();
//
// //
// // Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// // Service Routines (ISR).
// //
// Interrupt_initVectorTable();
//
// //
// // Enable Global Interrupt (INTM) and realtime interrupt (DBGM)
// //
// EINT;
// ERTM;
//
// //
// // Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// // ISR functions found within this file.
// // This registers the interrupt handler in PIE vector table.
// //
// Interrupt_register(INT_CANA0, &canISR);
//
//
// //
// // Enable the CAN interrupt signal
// //
// Interrupt_enable(INT_CANA0);
// CAN_enableGlobalInterrupt(CANA_BASE, CAN_GLOBAL_INT_CANINT0);
//
// CAN_disableTestMode(CANA_BASE);
//
//
// //
// // Enable CAN test mode with external loopback
// // 允许外部环回测试
//// CAN_enableTestMode(CANA_BASE, CAN_TEST_EXL);
//// CAN_enableTestMode(CANB_BASE, CAN_TEST_EXL);
//
// //
// // Initialize the transmit message object used for sending CAN messages.
// // Message Object Parameters:
// // Message Object ID Number: 1 消息对象(邮箱) ID(1-32) 每个 CAN 控制器有 32 个消息对象(邮箱)。
// // Message Identifier: 0x1 CAN的ID(11 位长度或 29 位长度,取决于帧类型)。
// // Message Frame: Standard 帧类型:标准帧(11 位 ID)或扩展帧(29 位 ID)。
// // Message Type: Transmit 消息类型:发送、接收、远程请求等。
// // Message ID Mask: 0x0 标识符过滤掩码,用于接收时匹配目标消息。
// // Message Object Flags: Transmit Interrupt 标志位组合(中断使能、过滤规则、FIFO 配置等)。
// // Message Data Length: 4 Bytes 数据长度(0-8 字节),对接收邮箱无效,仅用于发送。
// // 配置 CAN 控制器的消息对象(Mailbox) 此为发送
//
// CAN_setupMessageObject(CANA_BASE, TX_MSG_OBJ_ID, 0x131, CAN_MSG_FRAME_EXT,
// CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX, 0, CAN_MSG_OBJ_NO_FLAGS,
// MSG_DATA_LENGTH);
//
//
// //
// // Initialize the receive message object used for receiving CAN messages.
// // Message Object Parameters:
// // Message Object ID Number: 2
// // Message Identifier: 0x1
// // Message Frame: Standard
// // Message Type: Receive
// // Message ID Mask: 0x0
// // Message Object Flags: Receive Interrupt
// // Message Data Length: 4 Bytes (Note that DLC field is a "don't care"
// // for a Receive mailbox)
// // 配置 CAN 控制器的消息对象(Mailbox) 此为接收
// CAN_setupMessageObject(CANA_BASE, RX_MSG_OBJ_ID, 0x1314, CAN_MSG_FRAME_EXT,
// CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX, 0, CAN_MSG_OBJ_RX_INT_ENABLE,
// MSG_DATA_LENGTH);
//
//
// //
// // Start CAN module operations
// //
// CAN_startModule(CANA_BASE);
//
//
// //
// // Loop Forever - A new message will be sent once per second.
// //
// for(;;)
// {
// CAN_sendMessage(CANA_BASE, TX_MSG_OBJ_ID, MSG_DATA_LENGTH,
// txMsgData);
// Example_PassCount++;
//
// //
// // Delay 1 second before continuing
// //
// DEVICE_DELAY_US(1000000);
//
// //
// // Increment the value in the transmitted message data.
// //
// txMsgData[0] += 0x01;
// txMsgData[1] += 0x01;
// txMsgData[2] += 0x01;
// txMsgData[3] += 0x01;
// txMsgData[4] += 0x01;
// txMsgData[5] += 0x01;
// txMsgData[6] += 0x01;
// txMsgData[7] += 0x01;
//
// //
// // Reset data if exceeds a byte
// //
// if(txMsgData[0] > 0xFF)
// {
// txMsgData[0] = 0;
// }
// if(txMsgData[1] > 0xFF)
// {
// txMsgData[1] = 0;
// }
// if(txMsgData[2] > 0xFF)
// {
// txMsgData[2] = 0;
// }
// if(txMsgData[3] > 0xFF)
// {
// txMsgData[3] = 0;
// }
// if(txMsgData[4] > 0xFF)
// {
// txMsgData[4] = 0;
// }
// if(txMsgData[5] > 0xFF)
// {
// txMsgData[5] = 0;
// }
// if(txMsgData[6] > 0xFF)
// {
// txMsgData[6] = 0;
// }
// if(txMsgData[7] > 0xFF)
// {
// txMsgData[7] = 0;
// }
// }
//}
//
////
//// CAN ISR - The interrupt service routine called when a CAN interrupt is
//// triggered. It checks for the cause of the interrupt, and
//// maintains a count of all messages that have been transmitted.
////
//__interrupt void
//canISR(void)
//{
// uint32_t status;
// ISR_Count++;
// //
// // Read the CAN interrupt status to find the cause of the interrupt
// // 返回产生中断的寄存器的值 进而判断中断原因
// status = CAN_getInterruptCause(CANA_BASE);
//
// //
// // If the cause is a controller status interrupt, then get the status
// // 若是status中断读取控制器状态寄存器
// if(status == CAN_INT_INT0ID_STATUS)
// {
// //
// // Read the controller status. This will return a field of status
// // error bits that can indicate various errors. Error processing
// // is not done in this example for simplicity. Refer to the
// // API documentation for details about the error status bits.
// // The act of reading this status will clear the interrupt.
// // 读取Error and Status Register(手册里是CAN_ES)
// status = CAN_getStatus(CANA_BASE);
//
// // 检查是否有错误(排除正常标志位 TXOK 和 RXOK)
// // Check to see if an error occurred.
// // CAN_STATUS_TXOK | CAN_STATUS_RXOK=0x18=0001 1000
// // ~(CAN_STATUS_TXOK | CAN_STATUS_RXOK)=1110 0111是为了排除正常标志位 TXOK 和 RXOK
// // bit2-0是LEC(Last Error Code),除了0(无错误)和7(CAN_ES读取后的复位值)剩下的均是错误
// if(((status & ~(CAN_STATUS_RXOK)) != 7) &&
// ((status & ~(CAN_STATUS_RXOK)) != 0))
// {
// //
// // Set a flag to indicate some errors may have occurred.
// //
// errorFlag = 1;
// }
// }
// //
// // Check if the cause is the receive message object 2
// // 判断中断原因是否是RX
// else if(status == RX_MSG_OBJ_ID)
// {
// //
// // Get the received message
// //
//
// CAN_readMessage(CANA_BASE, RX_MSG_OBJ_ID, rxMsgData);
// GPIO_togglePin(133);
//
// txMsgData[0] = 0x55;
// txMsgData[1] = 0x55;
// txMsgData[2] = 0x55;
// txMsgData[3] = 0x55;
// txMsgData[4] = 0x55;
// txMsgData[5] = 0x55;
// txMsgData[6] = 0x55;
// txMsgData[7] = 0x55;
//
// CAN_sendMessage(CANA_BASE, TX_MSG_OBJ_ID, MSG_DATA_LENGTH,
// txMsgData);
// GPIO_togglePin(99);
//
// //
// // Getting to this point means that the RX interrupt occurred on
// // message object 2, and the message RX is complete. Clear the
// // message object interrupt.
// //
// CAN_clearInterruptStatus(CANA_BASE, RX_MSG_OBJ_ID);
//
// //
// // Increment a counter to keep track of how many messages have been
// // received. In a real application this could be used to set flags to
// // indicate when a message is received.
// //
// rxMsgCount++;
//
// //
// // Since the message was received, clear any error flags.
// //
// errorFlag = 0;
// }
//
// //
// // If something unexpected caused the interrupt, this would handle it.
// //
// else
// {
// //
// // Spurious interrupt handling can go here.
// //
// }
//
// //
// // Clear the global interrupt flag for the CAN interrupt line
// //
// CAN_clearGlobalInterruptStatus(CANA_BASE, CAN_GLOBAL_INT_CANINT0);
//
// //
// // Acknowledge this interrupt located in group 9
// //
// Interrupt_clearACKGroup(INTERRUPT_ACK_GROUP9);
//}
#include "driverlib.h"
#include "device.h"
// 主控为发送数据给开发板,开发板再返回55给主控
// 此为开发板程序
// Defines
//
#define MSG_DATA_LENGTH 8
#define TX_MSG_OBJ_ID 1
#define RX_MSG_OBJ_ID 2
//
// Globals
//
volatile uint32_t txMsgCount = 0;
volatile uint32_t rxMsgCount = 0;
volatile uint32_t errorFlag = 0;
uint32_t ISR_Count = 0;
uint16_t txMsgData[MSG_DATA_LENGTH];
uint16_t rxMsgData[MSG_DATA_LENGTH];
//
// Function Prototypes
//
__interrupt void canISR(void);
//
// Main
//
void main(void)
{
//
// Initialize device clock and peripherals
//
Device_init();
//
// Initialize GPIO and configure GPIO pins for CANTX/CANRX
//
Device_initGPIO();
GPIO_setPinConfig(DEVICE_GPIO_CFG_CANRXB);
GPIO_setPinConfig(DEVICE_GPIO_CFG_CANTXB);
//LED收到上位机命令翻转
GPIO_setMasterCore(133, GPIO_CORE_CPU1);//CPU1控制
GPIO_setPinConfig(GPIO_133_GPIO133);//配置为普通GPIO
GPIO_writePin(133,1);
GPIO_setDirectionMode(133, GPIO_DIR_MODE_OUT);
GPIO_setPadConfig(133, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);//默认配置,通常表示标准的推挽输出(push-pull output)或悬空输入(floating input)
//LED发送翻转
GPIO_setMasterCore(99, GPIO_CORE_CPU1);//CPU1控制
GPIO_setPinConfig(GPIO_99_GPIO99);//配置为普通GPIO
GPIO_writePin(99,1);
GPIO_setDirectionMode(99, GPIO_DIR_MODE_OUT);
GPIO_setPadConfig(99, GPIO_PIN_TYPE_STD);//默认配置,通常表示标准的推挽输出(push-pull output)或悬空输入(floating input)
//
// Initialize the CAN controller
//
// Puts the module in Initialization mode, Disables the parity function
// Initializes the MBX RAM, Initiates a S/W reset of the module
// Seeks write-access to configuration registers.
// 初始化CAN控制器 将模块置于初始化模式,禁用奇偶校验功能初始化MBX RAM,启动模块的S/W复位寻求对配置寄存器的写访问。
CAN_initModule(CANB_BASE);
//
// Set up the CAN bus bit rate to 500 kbps
// Refer to the Driver Library User Guide for information on how to set
// tighter timing control. Additionally, consult the device data sheet
// for more information about the CAN module clocking.
// CAN比特率为500kbps
// 20为bitTime(时间量子),每个CAN位(Bit)的时间由20个时间量子组成(范围:8-25)
// 波特率为500k,则发送一位时间=1/500k=2000ns,所以每个bitTime为2000ns/20=100ns
CAN_setBitRate(CANB_BASE, DEVICE_SYSCLK_FREQ, 1000000, 20);
//
// Enable interrupts on the CAN peripheral.
// Enables Interrupt line 0, Error & Status Change interrupts in CAN_CTL
// register.
// 允许产生中断线0中断(status、error、mb(mb中断允许在RX的CAN_setupMessageObject中:CAN_MSG_OBJ_RX_INT_ENABLE))、错误中断、状态变化中断(控制器状态变化?)
CAN_enableInterrupt(CANB_BASE, CAN_INT_IE0 | CAN_INT_ERROR |
CAN_INT_STATUS);
//
// Initialize PIE and clear PIE registers. Disables CPU interrupts.
//
Interrupt_initModule();
//
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
//
Interrupt_initVectorTable();
//
// Enable Global Interrupt (INTM) and realtime interrupt (DBGM)
//
EINT;
ERTM;
//
// Interrupts that are used in this example are re-mapped to
// ISR functions found within this file.
// This registers the interrupt handler in PIE vector table.
//
Interrupt_register(INT_CANB0, &canISR);
//
// Enable the CAN interrupt signal
//
Interrupt_enable(INT_CANB0);
CAN_enableGlobalInterrupt(CANB_BASE, CAN_GLOBAL_INT_CANINT0);
CAN_disableTestMode(CANB_BASE);
//
// Enable CAN test mode with external loopback
// 允许外部环回测试
// CAN_enableTestMode(CANA_BASE, CAN_TEST_EXL);
// CAN_enableTestMode(CANB_BASE, CAN_TEST_EXL);
//
// Initialize the transmit message object used for sending CAN messages.
// Message Object Parameters:
// Message Object ID Number: 1 消息对象(邮箱) ID(1-32) 每个 CAN 控制器有 32 个消息对象(邮箱)。
// Message Identifier: 0x1 CAN的ID(11 位长度或 29 位长度,取决于帧类型)。
// Message Frame: Standard 帧类型:标准帧(11 位 ID)或扩展帧(29 位 ID)。
// Message Type: Transmit 消息类型:发送、接收、远程请求等。
// Message ID Mask: 0x0 标识符过滤掩码,用于接收时匹配目标消息。
// Message Object Flags: Transmit Interrupt 标志位组合(中断使能、过滤规则、FIFO 配置等)。
// Message Data Length: 4 Bytes 数据长度(0-8 字节),对接收邮箱无效,仅用于发送。
// 配置 CAN 控制器的消息对象(Mailbox) 此为发送
CAN_setupMessageObject(CANB_BASE, TX_MSG_OBJ_ID, 0x131, CAN_MSG_FRAME_EXT,
CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_TX, 0, CAN_MSG_OBJ_NO_FLAGS,
MSG_DATA_LENGTH);
//
// Initialize the receive message object used for receiving CAN messages.
// Message Object Parameters:
// Message Object ID Number: 2
// Message Identifier: 0x1
// Message Frame: Standard
// Message Type: Receive
// Message ID Mask: 0x0
// Message Object Flags: Receive Interrupt
// Message Data Length: 4 Bytes (Note that DLC field is a "don't care"
// for a Receive mailbox)
// 配置 CAN 控制器的消息对象(Mailbox) 此为接收
CAN_setupMessageObject(CANB_BASE, RX_MSG_OBJ_ID, 0x1314, CAN_MSG_FRAME_EXT,
CAN_MSG_OBJ_TYPE_RX, 0, CAN_MSG_OBJ_RX_INT_ENABLE,
MSG_DATA_LENGTH);
//
// Start CAN module operations
//
CAN_startModule(CANB_BASE);
//
// Loop Forever - A new message will be sent once per second.
//
for(;;)
{
CAN_sendMessage(CANB_BASE, TX_MSG_OBJ_ID, MSG_DATA_LENGTH,
txMsgData);
Example_PassCount++;
//
// Delay 1 second before continuing
//
DEVICE_DELAY_US(1000000);
//
// Increment the value in the transmitted message data.
//
txMsgData[0] += 0x01;
txMsgData[1] += 0x01;
txMsgData[2] += 0x01;
txMsgData[3] += 0x01;
txMsgData[4] += 0x01;
txMsgData[5] += 0x01;
txMsgData[6] += 0x01;
txMsgData[7] += 0x01;
//
// Reset data if exceeds a byte
//
if(txMsgData[0] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[0] = 0;
}
if(txMsgData[1] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[1] = 0;
}
if(txMsgData[2] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[2] = 0;
}
if(txMsgData[3] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[3] = 0;
}
if(txMsgData[4] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[4] = 0;
}
if(txMsgData[5] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[5] = 0;
}
if(txMsgData[6] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[6] = 0;
}
if(txMsgData[7] > 0xFF)
{
txMsgData[7] = 0;
}
}
}
//
// CAN ISR - The interrupt service routine called when a CAN interrupt is
// triggered. It checks for the cause of the interrupt, and
// maintains a count of all messages that have been transmitted.
//
__interrupt void
canISR(void)
{
uint32_t status;
ISR_Count++;
//
// Read the CAN interrupt status to find the cause of the interrupt
// 返回产生中断的寄存器的值 进而判断中断原因
status = CAN_getInterruptCause(CANB_BASE);
//
// If the cause is a controller status interrupt, then get the status
// 若是status中断读取控制器状态寄存器
if(status == CAN_INT_INT0ID_STATUS)
{
//
// Read the controller status. This will return a field of status
// error bits that can indicate various errors. Error processing
// is not done in this example for simplicity. Refer to the
// API documentation for details about the error status bits.
// The act of reading this status will clear the interrupt.
// 读取Error and Status Register(手册里是CAN_ES)
status = CAN_getStatus(CANB_BASE);
// 检查是否有错误(排除正常标志位 TXOK 和 RXOK)
// Check to see if an error occurred.
// CAN_STATUS_TXOK | CAN_STATUS_RXOK=0x18=0001 1000
// ~(CAN_STATUS_TXOK | CAN_STATUS_RXOK)=1110 0111是为了排除正常标志位 TXOK 和 RXOK
// bit2-0是LEC(Last Error Code),除了0(无错误)和7(CAN_ES读取后的复位值)剩下的均是错误
if(((status & ~(CAN_STATUS_RXOK)) != 7) &&
((status & ~(CAN_STATUS_RXOK)) != 0))
{
//
// Set a flag to indicate some errors may have occurred.
//
errorFlag = 1;
}
}
//
// Check if the cause is the receive message object 2
// 判断中断原因是否是RX
else if(status == RX_MSG_OBJ_ID)
{
//
// Get the received message
//
CAN_readMessage(CANB_BASE, RX_MSG_OBJ_ID, rxMsgData);
GPIO_togglePin(133);
txMsgData[0] = 0x55;
txMsgData[1] = 0x55;
txMsgData[2] = 0x55;
txMsgData[3] = 0x55;
txMsgData[4] = 0x55;
txMsgData[5] = 0x55;
txMsgData[6] = 0x55;
txMsgData[7] = 0x55;
CAN_sendMessage(CANB_BASE, TX_MSG_OBJ_ID, MSG_DATA_LENGTH,
txMsgData);
GPIO_togglePin(99);
//
// Getting to this point means that the RX interrupt occurred on
// message object 2, and the message RX is complete. Clear the
// message object interrupt.
//
CAN_clearInterruptStatus(CANB_BASE, RX_MSG_OBJ_ID);
//
// Increment a counter to keep track of how many messages have been
// received. In a real application this could be used to set flags to
// indicate when a message is received.
//
rxMsgCount++;
//
// Since the message was received, clear any error flags.
//
errorFlag = 0;
}
//
// If something unexpected caused the interrupt, this would handle it.
//
else
{
//
// Spurious interrupt handling can go here.
//
}
//
// Clear the global interrupt flag for the CAN interrupt line
//
CAN_clearGlobalInterruptStatus(CANB_BASE, CAN_GLOBAL_INT_CANINT0);
//
// Acknowledge this interrupt located in group 9
//
Interrupt_clearACKGroup(INTERRUPT_ACK_GROUP9);
}
