主题中讨论的其他器件:TMP117、 SysConfig、 BOOSTXL-SENSORS、 BOOSTXL-BASSENSORS、 MSP430F5528
您好!
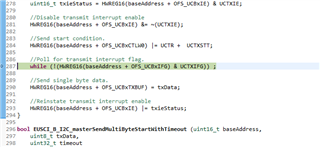
是否有任何用于 MSP430FR5969微控制器与 TMP117温度传感器通信的 I2C 示例代码。 我已经从 SysConfig 工具中下载了 tmp117.c、tmp117.h、mcu.c、mcu.h 和 main.c、但 mcu.c 文件必须针对 MSP430FR5969 I2C 外设进行修改。 任何示例代码都将非常有帮助、谢谢。