Other Parts Discussed in Thread: C2000WARE
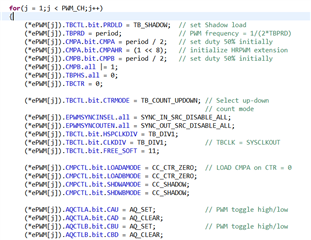
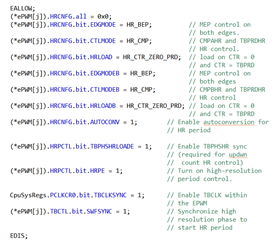
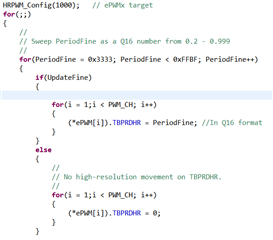
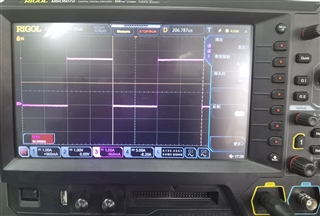
在使用C:\ti\c2000\C2000Ware_3_04_00_00\device_support\f28002x\examples\hrpwm\hrpwm_ex2_prdupdown_sfo_v8.c例程时,PWM 5Mhz频率下通过示波器能清楚观测到周期边缘位置的变化,当PWM使用50Khz频率时,基本在示波器上看不到周期边缘有变化,请问是因为高精度PWM对于其频率有最低限度要求吗?如果不是的话为什么50Khz时观测不到变化