DSP双核IPC通信,CPU1同样一个数组readData,我把他放在MSGRAM_CPU1_TO_CPU2里面,传输给CPU2,CPU2读取到的readData地址正确,但是我把数组readData放在RAMGS0中,CPU2读取到的readData地址错误,本来地址应该是0x00C000,现在是0x8000C000,这是为什么呢?我CPU1和CPU2的CMD文件都定义了RAMGS0的起始位置和长度,RAMGS0由CPU1控制。
此外我还有一个问题,就是我在CPU1和CPU2都定义了GSRAM0的话,他们是共享这一片GSRAM0还是说CPU1有一块GSRAM0,CPU2有另外的GSRAM0呢?

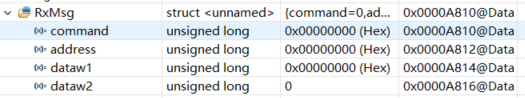 在MSGRAM_CPU1_TO_CPU2里面,传输给CPU2,若是传输的数组大一点例如uint32_t readData[70];,,CPU2的RxMsg都为0了。这是为什么呢??
在MSGRAM_CPU1_TO_CPU2里面,传输给CPU2,若是传输的数组大一点例如uint32_t readData[70];,,CPU2的RxMsg都为0了。这是为什么呢??